Remote Ischemic Postconditioning Improve Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Induced Cognitive Dysfunction through Suppressing Mitochondrial Apoptosis in Hippocampus via TK/BK/B2R-Mediated PI3K/AKT
- PMID: 40229456
- PMCID: PMC12289851
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-025-04864-y
Remote Ischemic Postconditioning Improve Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Induced Cognitive Dysfunction through Suppressing Mitochondrial Apoptosis in Hippocampus via TK/BK/B2R-Mediated PI3K/AKT
Abstract
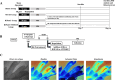
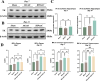
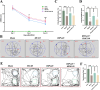
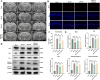
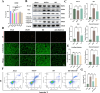
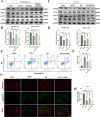
Remote ischemic postconditioning (RIPostC) is known to improve motor function recovery in animal models, but its efficacy in alleviating cognitive impairment caused by ischemic stroke remains unclear. This study aims to investigate the beneficial role of RIPostC in recovering cognitive impairment induced by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury (CIRI). Building upon our previous research findings, we proved that the TK/BK/B2R pathway is crucial for understanding the crosstalk between cognitive impairment and RIPostC. Additionally, in vitro experiments were conducted using the oxygen glucose deprivation/re-oxygenation (OGD/r) HT-22 cell model, which revealed that the mechanism by which RIPostC suppressed mitochondrial apoptosis was mainly through the activation of the B2R/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, thereby protecting neurons in the ischemic hippocampus from ischemic damage. To investigate the effect of RIPostC on cognitive function recovery following ischemic stroke, we established a rat model using left middle cerebral artery occlusion reperfusion (MCAO/r). 48 h after MCAO/r, rats were subjected to 3 circles of RIPostC therapy daily for 12 consecutive days. HOE140 was used to antagonize the bradykinin 2 receptor (B2R). Cognitive function was assessed using a modified neurological severity score, the Morris water maze, and the novel object recognition test. Local infarct volume in the hippocampus was measured through MRI scanning. The apoptosis rate of hippocampal neurons was quantified using TUNEL staining. Protein expression levels of kallikrein (TK) and mitochondrial apoptosis-related proteins, Cyt c, Bcl-2, Bax, cleaved caspase-3, and cleaved caspase-9, were detected in ischemic hippocampal tissue using Western blot (WB). The expression of bradykinin (BK) in serum and the ischemic penumbra was measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent (ELISA) assay. In the cell experiments, the HT-22 cell line and OGD/r model were used to simulate in vitro hippocampal ischemia. WB was performed to detect the expression of apoptosis-related proteins and PI3K/AKT pathway proteins. The apoptosis rate of HT-22 cells was detected using Annexin-V/PI flow cytometry and a cell viability kit. JC-1 staining and reactive oxygen species staining were used to evaluate mitochondrial condition. The PI3K/AKT pathway was inhibited using LY294002. RIPostC significantly upregulated the concentrations of TK and BK in the ischemic hippocampus. Behavioral function tests demonstrated that daily RIPostC therapy for 12 days significantly promoted cognitive function recovery in MCAO/r rats. Through MRI analysis, we found that RIPostC therapy effectively reduced the infarct volume in the hippocampus. Additionally, TUNEL staining and WB results of apoptosis-related proteins showed that RIPostC therapy significantly reduced apoptosis of hippocampal neurons. However, the therapeutic effect of RIPostC was reversed by the B2R antagonist HOE14, indicating that the TK/BK/B2R pathway mediated the neuroprotective effect of RIPostC. Cell experiments further confirmed that BK/B2R significantly attenuated mitochondrial apoptosis induced by ischemia-hypoxia injury in HT-22 cells. In vivo and in vitro results from WB demonstrated that the BK/B2R pathway activated the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Finally, the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 reversed the anti-apoptotic effect induced by BK/B2R. RIPostC therapy effectively inhibited mitochondrial apoptosis of hippocampal neurons and significantly alleviated cognitive dysfunction associated with CIRI by regulating the TK/BK/B2R-medated PI3K/AKT pathway. In conclusion, RIPostC represents a promising therapeutic strategy for combating cognitive dysfunction by inhibiting cell apoptosis in hippocampus. Moreover, our results suggest that RIPostC may have a broader protective effect against apoptosis in other ischemia-reperfusion-related diseases.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury; Cognitive dysfunction; Hippocampus; Remote ischemic postconditioning.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Puerarin alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (CIR)-induced neurocyte oxidative stress and apoptosis via DNA demethylation-mediated PI3K/Akt activation.Phytomedicine. 2025 Sep;145:157094. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.157094. Epub 2025 Jul 22. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40714421
-
Activation of BDNF-TrkB-PI3K-AKT signaling pathway by Tong-Qiao-Huo-Xue Decoction facilitates nerve regeneration and mitigates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury.Phytomedicine. 2025 Sep;145:156966. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156966. Epub 2025 Jun 12. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40578040
-
Deciphering the neuroprotective mechanisms of RACK1 in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury: Pioneering insights into mitochondrial autophagy and the PINK1/Parkin axis.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Aug;30(8):e14836. doi: 10.1111/cns.14836. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39097918 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of significant parameters in remote ischemic postconditioning for ischemic stroke in experimental models: A systematic review and meta-analysis study.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022 Oct;28(10):1492-1508. doi: 10.1111/cns.13925. Epub 2022 Jul 27. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022. PMID: 35896511 Free PMC article.
-
MAPK, PI3K/Akt Pathways, and GSK-3β Activity in Severe Acute Heart Failure in Intensive Care Patients: An Updated Review.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025 Jul 10;12(7):266. doi: 10.3390/jcdd12070266. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025. PMID: 40710791 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hankey GJ (2017) Stroke. Lancet 389(10069):641–654 - PubMed
-
- Rost NS et al (2022) Post-stroke cognitive impairment and dementia. Circ Res 130(8):1252–1271 - PubMed
-
- Huang YY et al (2022) Post-stroke cognitive impairment: epidemiology, risk factors, and management. J Alzheimers Dis 86(3):983–999 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

