Multiparametric MRI-based radiomics and clinical nomogram predicts the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after postoperative adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization
- PMID: 40229712
- PMCID: PMC11995621
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-025-14079-y
Multiparametric MRI-based radiomics and clinical nomogram predicts the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after postoperative adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization
Abstract
Background: This study was undertaken to develop and validate a radiomics model based on multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for predicting recurrence in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) following postoperative adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization (PA-TACE).
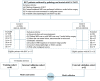
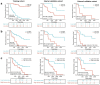
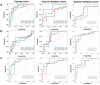
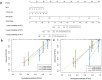
Methods: In this retrospective study, 149 HCC patients (81 for training, 36 for internal validation, 32 for external validation) treated with PA-TACE were included in two medical centers. Multiparametric radiomics features were extracted from three MRI sequences. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO)-COX regression was utilized to select radiomics features. Optimal clinical characteristics selected by multivariate Cox analysis were integrated with Rad-score to develop a recurrence-free survival (RFS) prediction model. The model performance was evaluated by time-dependent receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, Harrell's concordance index (C-index), and calibration curve.
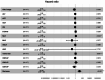
Results: Fifteen optimal radiomic features were selected and the median Rad-score value was 0.434. Multivariate Cox analysis indicated that neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) (hazard ratio (HR) = 1.49, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.1-2.1, P = 0.022) and tumor size (HR = 1.28, 95% CI: 1.1-1.5, P = 0.001) were the independent predictors of RFS after PA-TACE. A combined model was established by integrating Rad-score, NLR, and tumor size in the training cohort (C-index 0.822; 95% CI 0.805-0.861), internal validation cohort (0.823; 95% CI 0.771-0.876) and external validation cohort (0.846; 95% CI 0.768-0.924). The calibration curve exhibited a satisfactory correspondence.
Conclusion: A multiparametric MRI-based radiomics model can predict RFS of HCC patients receiving PA-TACE and a nomogram can be served as an individualized tool for prognosis.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Nomogram; Postoperative adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization; Radiomics; Recurrence.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval: This retrospective study was received approval by the Ethical Committee of Lishui Hospital of Zhejiang University and was carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Consent to participate: The requirement for informed consent was waived by the Ethical Committee of Lishui Hospital of Zhejiang University due to the retrospective nature of the research. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Computed tomography radiomic features and clinical factors predicting the response to first transarterial chemoembolization in intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2024 Aug;23(4):361-369. doi: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2023.06.011. Epub 2023 Jul 5. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2024. PMID: 37429785
-
Prediction of tumor response via a pretreatment MRI radiomics-based nomogram in HCC treated with TACE.Eur Radiol. 2021 Oct;31(10):7500-7511. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07910-0. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33860832 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a computed tomography-based radiomics nomogram for prediction of transarterial chemoembolization refractoriness in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Jan 14;27(2):189-207. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i2.189. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33510559 Free PMC article.
-
Multiparametric radiomic analysis of MRI for predicting satellite nodules and recurrence-free survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Magn Reson Imaging. 2025 Oct;122:110450. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2025.110450. Epub 2025 Jun 16. Magn Reson Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40532770 Review.
-
Diagnostic Efficacy of Contrast-Enhanced MRI in Detecting Residual or Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Transarterial Chemoembolization: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020 Oct;52(4):1019-1028. doi: 10.1002/jmri.26970. Epub 2019 Nov 1. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020. PMID: 31675170
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72(1):7–33. - PubMed
-
- Imamura H, Matsuyama Y, Tanaka E, Ohkubo T, Hasegawa K, Miyagawa S, Sugawara Y, Minagawa M, Takayama T, Kawasaki S, Makuuchi M. Risk factors contributing to early and late phase intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. J Hepatol. 2003;38(2):200–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

