The effect of low-carbohydrate diets, based on changes in intake of dietary saturated fats on circulating TNF-α and interleukin- 6 levels in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 40229854
- PMCID: PMC11995482
- DOI: 10.1186/s40795-025-01062-w
The effect of low-carbohydrate diets, based on changes in intake of dietary saturated fats on circulating TNF-α and interleukin- 6 levels in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Low-carbohydrate diets (LCDs) have been associated with inflammation while there is still conflicting evidence regarding the effects of this type of diet on inflammatory markers and the clinical benefit of them remains uncertain. So, we aimed to ascertain the effects of LCDs on serum concentrations of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin- 6 (IL- 6) by performing a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials (RCTs).
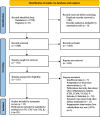
Methods: The online databases PubMed, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), EMBASE, Web of Science, and Scopus were comprehensively searched up to February 2024, to find pertinent RCTs. Pooled weighted mean difference (WMD) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using the random-effects model.
Results: This meta-analysis of 33 studies assessed a total of 2106 adults irrespective of their health status. Compared with control group, participants on LCDs experienced a decline in IL- 6 levels (WMD: - 0.31 pg/mL; 95% CI: - 0.49 to - 0.12; P = 0.001). However, no significant effect was revealed for TNF-α (WMD: - 0.02 pg/mL; 95% CI: - 0.08 to - 0.03; P = 0.449). Stratification analyses indicated that beneficial effects of LCDs on inflammatory cytokines (WMD: - 0.28 pg/mL; 95% CI: - 0.47 to - 0.10; P = 0.003, WMD: - 0.26 pg/mL; 95% CI: - 0.48 to - 0.03; P = 0.027, for TNF-α and IL- 6, respectively) were stronger when carbohydrate intake was < 10%. The results of Meta-regression analyses suggested that baseline level of both markers remained as a strong predictor of the effect size (P = 0.038 and P = 0.001 for TNF-α and IL- 6, respectively).
Conclusion: Adherence to LCDs appeared to be effective at improving inflammatory cytokines particularly, when carbohydrate intake was restricted to less than 10% of total energy. Nevertheless, further rigorously designed clinical trials considering factors such as race and genetic, the sources and quality of dietary carbohydrates, protein, and fat are required to gain a deeper understanding of the impact of LCDs on inflammatory markers.
Trial registration: PROSPERO, registration no: CRD42023387452.
Keywords: Carbohydrate restriction; Inflammation; Interleukin- 6; Low-carbohydrate diet; Meta-analysis; TNF-α.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of a ketogenic diet on inflammation-related markers: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Nutr Rev. 2025 Jan 1;83(1):40-58. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuad175. Nutr Rev. 2025. PMID: 38219223
-
The Effect of Whole-Grain Intake on Biomarkers of Subclinical Inflammation: A Comprehensive Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Adv Nutr. 2020 Jan 1;11(1):52-65. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmz063. Adv Nutr. 2020. PMID: 31301131 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the Efficacy and Safety of Low-Carbohydrate Diets with Low-Fat Diets for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.Int J Endocrinol. 2021 Dec 6;2021:8521756. doi: 10.1155/2021/8521756. eCollection 2021. Int J Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34912453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Almond Consumption on Inflammatory Biomarkers in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.Adv Nutr. 2022 Oct 2;13(5):1462-1475. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmab158. Adv Nutr. 2022. PMID: 34967837 Free PMC article.
-
Does omega-3 PUFAs supplementation improve metabolic syndrome and related cardiovascular diseases? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Sep;64(26):9455-9482. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2212817. Epub 2023 May 24. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 37222574
Cited by
-
Effect of Low-Carbohydrate Diets on C-Reactive Protein Level in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jul 18;13(7):e70566. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70566. eCollection 2025 Jul. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40688603 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gregor MF, Hotamisligil GS. Inflammatory Mechanisms in Obesity. Annual Review of Immunology. 2011;29(Volume 29, 2011):415–45. - PubMed
-
- Stouthard JM, Romijn JA, Van der Poll T, Endert E, Klein S, Bakker PJ, et al. Endocrinologic and metabolic effects of interleukin-6 in humans. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism. 1995;268(5):E813–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources