Extracellular vesicle-derived miRNA-mediated cell-cell communication inference for single-cell transcriptomic data with miRTalk
- PMID: 40229908
- PMCID: PMC11998287
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-025-03566-x
Extracellular vesicle-derived miRNA-mediated cell-cell communication inference for single-cell transcriptomic data with miRTalk
Abstract
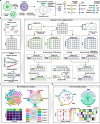
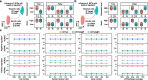
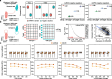
MicroRNAs are released from cells in extracellular vesicles (EVs), representing an essential mode of cell-cell communication (CCC) via a regulatory effect on gene expression. Single-cell RNA-sequencing technologies have ushered in an era of elucidating CCC at single-cell resolution. Herein, we present miRTalk, a pioneering approach for inferring CCC mediated by EV-derived miRNA-target interactions (MiTIs). The benchmarking against simulated and real-world datasets demonstrates the superior performance of miRTalk, and the application to four disease scenarios reveals the in-depth MiTI-mediated CCC mechanisms. Collectively, miRTalk can infer EV-derived MiTI-mediated CCC with scRNA-seq data, providing new insights into the intercellular dynamics of biological processes.
Keywords: Cell–cell communication; Extracellular vesicle; MiRNA; ScRNA-seq; Spatial transcriptomics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Wang J, Li L, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Zhu Y, Zhang C, Bi Y. Extracellular vesicles mediate the communication of adipose tissue with brain and promote cognitive impairment associated with insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2022;34(1264–1279): e1268. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82200725/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81930016/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- ZYYCXTD-D-202002/Innovation Team and Talents Cultivation Program of National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- 226-2023-00059/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- 226-2023-00114/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

