Genetic determinants and clinical significance of circulating and tumor-specific levels of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) in a Swedish breast cancer cohort
- PMID: 40230015
- PMCID: PMC12066007
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgaf020
Genetic determinants and clinical significance of circulating and tumor-specific levels of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) in a Swedish breast cancer cohort
Abstract
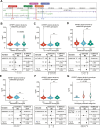
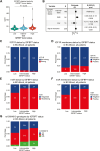
Previous research indicates that insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) protein levels in breast cancer tissue and blood are prognostic. However, genetic determinants of IGFBP7 in breast cancer remain largely unexplored. We examined IGFBP7 in a cohort of 1701 patients with first breast cancer from Sweden, enrolled prior to surgery 2002-16 and followed for up to 15 years. Genotyping was performed on blood samples using OncoArray. Tumor-specific protein levels of IGFBP7, insulin receptor (InsR), and IGF-I receptor (IGFIR) were assessed on tumor tissue microarrays in 964 patients. Furthermore, 275 patients had plasma IGFBP7 levels measured. A genetic proxy marker for circulating IGFBP7 levels was constructed from five candidate single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (rs6852762, rs1714014, rs9992658, rs10004910, and rs4865180) based on number of recessive genotypes. Age-adjusted linear regression was used to evaluate SNPs and tumor-specific IGFBP7 levels in relation to circulating IGFBP7 levels. Cox regression adjusted for age, tumor characteristics, and adjuvant treatments was used to assess associations with clinical outcomes. Circulating and tumor-specific IGFBP7 levels were significantly positively correlated. High circulating and genetically predicted IGFBP7 levels were associated with increased risk for distant metastasis and all-cause mortality. A significant interaction between high tumor-specific IGFBP7 levels and membrane-bound InsR resulted in a four-fold increased risk of breast cancer events and distant metastases. Both measured and genetically predicted IGFBP7 levels were independent prognostic biomarkers in breast cancer.
Keywords: IGFBP7; breast cancer; cohort study; genotype; prognostic biomarker.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Prognostic impact of tumor-specific insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) levels in breast cancer: a prospective cohort study.Carcinogenesis. 2021 Nov 12;42(11):1314-1325. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgab090. Carcinogenesis. 2021. PMID: 34606580 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-7 Is Positively Associated with Age, Obesity, Mortality, and Cancer in Postmenopausal Women.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2025 Jun 3;34(6):922-932. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-24-1644. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2025. PMID: 40152978
-
Genotypes and haplotypes in the insulin-like growth factors, their receptors and binding proteins in relation to plasma metabolic levels and mammographic density.BMC Med Genomics. 2010 Mar 19;3:9. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-3-9. BMC Med Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20302654 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3, genetic polymorphisms and mammographic density in premenopausal Mexican women: results from the ESMaestras cohort.Int J Cancer. 2014 Mar 15;134(6):1436-44. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28469. Epub 2013 Oct 5. Int J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24037648 Free PMC article.
-
Common genetic variation of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 1 (IGFBP-1), IGFBP-3, and acid labile subunit in relation to serum IGF-I levels and mammographic density.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010 Oct;123(3):843-55. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-0778-2. Epub 2010 Feb 14. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010. PMID: 20155489
References
-
- Godina C, Khazaei S, Tryggvadottir H. et al. Prognostic impact of tumor-specific insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) levels in breast cancer: a prospective cohort study. Carcinogenesis 2021;42:1314–25. https://doi.org/ 10.1093/carcin/bgab090 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rosendahl AH, Björner S, Ygland Rödström M. et al. Pre- and postoperative circulating IGF-I, IGFBP-3, and IGFBP-7 levels in relation to endocrine treatment and breast cancer recurrence: a nested case-control study. Front Oncol 2021;11:626058. https://doi.org/ 10.3389/fonc.2021.626058 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Godina C, Pollak MN, Jernström H.. Targeting IGF-IR improves neoadjuvant chemotherapy efficacy in breast cancers with low IGFBP7 expression. NPJ Precis Oncol 2024;8:212. https://doi.org/ 10.1038/s41698-024-00712-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yee D, Isaacs C, Wolf DM. et al. Ganitumab and metformin plus standard neoadjuvant therapy in stage 2/3 breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021;7:131. https://doi.org/ 10.1038/s41523-021-00337-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pollak M. The insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptor family in neoplasia: an update. Nat Rev Cancer 2012;12:159–69. https://doi.org/ 10.1038/nrc3215 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

