Influence of Resistance Training Variables and the Nordic Hamstring Exercise on Biceps Femoris Architectural Adaptations in Soccer Players: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 40230340
- PMCID: PMC11999990
- DOI: 10.1177/19417381251331607
Influence of Resistance Training Variables and the Nordic Hamstring Exercise on Biceps Femoris Architectural Adaptations in Soccer Players: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Context: Manipulation of resistance training variables influences the structural and functional adaptations of muscle, having a great impact on sport performance and hamstring injury prevention.
Objective: To analyze how the main resistance training variables affect the biceps femoris long head architecture in soccer players.
Data sources: Five databases were searched from inception to January 2024.
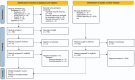
Study selection: Studies that included training intervention groups and measured muscle architecture adaptations before and after the training program in soccer players were included.
Study design: Systematic review with meta-analysis.
Level of evidence: Level 2.
Data extraction: Muscle thickness, fascicle length, and pennation angle were extracted from included studies as main outcomes.
Results: Six studies and 12 training groups (168 participants) were analyzed. The effects of Nordic hamstring exercise (NHE) against soccer interventions, volume of training, and frequency of training as independent variables were analyzed. NHE significantly improved biceps femoris long head fascicle length (P = 0.01). Training twice a week did not show significant differences compared with training once a week. Higher volumes of training (ie, >290 repetitions) in a period of 6 to 12 weeks with 57 repetitions per week demonstrated significant effects.
Conclusion: NHE lengthens the fascicle, especially if a sufficient volume (ie, >290 repetitions) and 2 days per week are performed. It is still unknown how the programming of some fundamental variables such as intensity, degree of effort, or exercise selection affects the muscle architecture of the biceps femoris long head.
Keywords: fascicle length; muscle architecture; muscle thickness; pennation angle; strength.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no potential conflicts of interest in the development and publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Preseason Training Program With the Nordic Hamstring Exercise Increases Eccentric Knee Flexor Strength and Fascicle Length in Professional Female Soccer Players.Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2021 Apr 1;16(2):459-467. doi: 10.26603/001c.19452. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2021. PMID: 33842041 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Nordic Hamstring Exercise Intervention Volume on Eccentric Strength and Muscle Architecture Adaptations: A Systematic Review and Meta-analyses.Sports Med. 2020 Jan;50(1):83-99. doi: 10.1007/s40279-019-01178-7. Sports Med. 2020. PMID: 31502142 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Eccentric Training on Biceps Femoris Architecture and Strength: A Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis.J Athl Train. 2020 May;55(5):501-514. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-194-19. Epub 2020 Mar 27. J Athl Train. 2020. PMID: 32216654 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in muscle architecture of biceps femoris induced by eccentric strength training with nordic hamstring exercise.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018 Jan;28(1):88-94. doi: 10.1111/sms.12877. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018. PMID: 28314091
-
Muscle Architecture, Morphology, and Mechanical and Functional Properties of Biceps Femoris Long Head in Professional Soccer Players with a Prior Healed Injured Hamstring.J Clin Med. 2022 Dec 5;11(23):7222. doi: 10.3390/jcm11237222. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36498796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al Attar WSA, Soomro N, Sinclair PJ, Pappas E, Sanders RH. Effect of injury prevention programs that include the Nordic hamstring exercise on hamstring injury rates in soccer players: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2017;47(5):907-916. - PubMed
-
- Blazevich AJ, Cannavan D, Coleman DR, Horne S. Influence of concentric and eccentric resistance training on architectural adaptation in human quadriceps muscles. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007;103(5):1565-1575. - PubMed
-
- Cadu J-P, Goreau V, Lacourpaille L. A very low volume of Nordic hamstring exercise increases maximal eccentric strength and reduces hamstring injury rate in professional soccer players. J Sport Rehabil. 2022;31(8):1061-1066. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials