Effects of opium on cholesterol metabolism in rats fed normal and high-fat/high-cholesterol diet
- PMID: 40230514
- PMCID: PMC11995082
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2025.102014
Effects of opium on cholesterol metabolism in rats fed normal and high-fat/high-cholesterol diet
Abstract
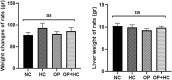
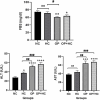
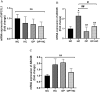
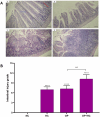
There is a misconception that opium can lower blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Hence, this study aimed to investigate the influences of opium on the expression of key cholesterol metabolism genes in the liver and intestine of rats receiving a cholesterol-rich diet. Male Wistar rats were randomly divided into four groups (n = 6): normal control, opium addiction, hypercholesterolemic diet, and opium addiction received hypercholesterolemic diet. After 28 days, the blood glucose levels, liver enzymes, and cholesterol in the rat's serum were measured. The cholesterol regulatory genes and transporters such as 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDL-R), cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase 1 (CYP7A1) (in liver tissue), and ATP Binding cassette subfamily g member 5 and 8 (ABCG5 and ABCG8), and Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 protein (NPC1L1) (in intestinal tissue) were measured. Intestinal morphological changes were also evaluated. Opium decreased serum glucose and total cholesterol levels (P < 0.05). In contrast, the levels of liver enzymes increased compared to the normal control group (P < 0.05). Histological examinations revealed that opium caused disorganization, deformation, and destruction of cells in intestinal tissue. Real-time PCR analysis demonstrated that opium increased the expression of LDL receptor genes, HMG-CoA reductase enzyme, and CYP7A1 in the liver compared to the normal control group (P < 0.05). The changes of ABCG8 and NPC1L1 transporters in intestinal tissue were not significant. Opium had beneficial effects on blood lipid and glucose levels, but histological findings indicated destructive effects on intestinal tissues.
Keywords: Cholesterol; Lipid; Opium; Rat.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Ebrahim Abbasi reports financial support was provided by Hamadan University of Medical Sciences Faculty of Health and Research Center for Health Sciences Department of Environmental Health Engineering. Ebrahim Abbasi reports a relationship with Hamadan University of Medical Sciences Faculty of Health and Research Center for Health Sciences Department of Environmental Health Engineering that includes:. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diosgenin regulates cholesterol metabolism in hypercholesterolemic rats by inhibiting NPC1L1 and enhancing ABCG5 and ABCG8.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2019 Aug;1864(8):1124-1133. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2019.04.010. Epub 2019 May 1. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2019. PMID: 31054325
-
The hypocholesterolemic activity of açaí (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) is mediated by the enhanced expression of the ATP-binding cassette, subfamily G transporters 5 and 8 and low-density lipoprotein receptor genes in the rat.Nutr Res. 2012 Dec;32(12):976-84. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2012.10.001. Epub 2012 Nov 1. Nutr Res. 2012. PMID: 23244543
-
Effect of garlic extract on some serum biochemical parameters and expression of npc1l1, abca1, abcg5 and abcg8 genes in the intestine of hypercholesterolemic mice.Indian J Biochem Biophys. 2013 Dec;50(6):500-4. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 2013. PMID: 24772974
-
Impact of a high-cholesterol diet on expression levels of Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 and intestinal transporters in rats and mice.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2016 Aug;41(4):457-63. doi: 10.1007/s13318-015-0269-2. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2016. PMID: 25716431
-
ABCG5/ABCG8 in cholesterol excretion and atherosclerosis.Clin Chim Acta. 2014 Jan 20;428:82-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.11.010. Epub 2013 Nov 16. Clin Chim Acta. 2014. PMID: 24252657 Review.
References
-
- Presley C.C., Lindsley C.W. DARK classics in chemical neuroscience: opium, a historical perspective. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018;9(10):2503–2518. - PubMed
-
- Merzaeipoor F., Azdaki N., Mohamadi G., Abasi E. The effects of opium addiction through different administration routes on inflammatory and coagulation factors. J. Kerman Univ. Med. Sci. 2013;20(3):292–300.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

