Deciphering the anti‑influenza potential of Eucommiae Cortex based on bioinformatics analysis: In silico and in vitro experiments
- PMID: 40230620
- PMCID: PMC11995446
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2025.12856
Deciphering the anti‑influenza potential of Eucommiae Cortex based on bioinformatics analysis: In silico and in vitro experiments
Abstract
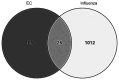
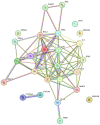
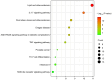
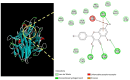
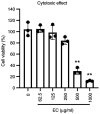
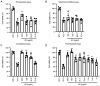
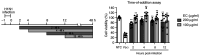
Influenza infections damage the airway and induce the innate immune response that contributes to hyper-inflammation. Eucommiae Cortex (EC) enhances immune function and suppresses inflammation. To determine potential compounds and targets of EC associated with influenza, bioinformatics analyses and experimental verification were employed. The active compounds of EC were retrieved from the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology database. The intersecting targets of EC and influenza were determined and examined using network pharmacology to analyze the relationship between the compounds and disease targets. The network identified three main compounds (quercetin, genistein and kaempferol) and four main targets (IL6, BCL2, IL1B and TNF). The ligand-target binding affinity was calculated by molecular docking, a computational method used in drug design to predict the interaction between the compound and protein target. The docking results revealed that kaempferol and TNF showed the strongest binding affinity. In vitro experiments confirmed the therapeutic effect of EC in influenza virus-infected Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Collectively, the present study identified the active compounds and potential targets of EC in influenza and suggested EC as a future influenza treatment.
Keywords: Eucommiae Cortex; bioinformatics; influenza; molecular docking; network pharmacology; systems biology.
Copyright © 2025, Spandidos Publications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
