CD121b-positive neutrophils predict immunosuppression in septic shock
- PMID: 40230851
- PMCID: PMC11994419
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1565797
CD121b-positive neutrophils predict immunosuppression in septic shock
Abstract
Background: Septic shock is linked with high mortality and significant long-term morbidity in survivors. However, the specific role of neutrophils in septic shock pathophysiology remains scarce in recent research.
Methods: Peripheral blood immune cells from healthy donors and patients with septic shock were analyzed using single-cell RNA sequencing and batch RNA sequencing. We measured serum CD121b in both patients and healthy donors. Peripheral immune cells were isolated and exposed to either a CD121b recombinant protein or a CD121b blocking antibody to evaluate the expression of inflammatory factors. Additionally, in a humanized mouse sepsis model, the expression of CD121b in neutrophils across different tissues was assessed following treatment with all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA).
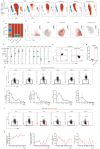
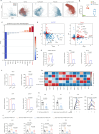
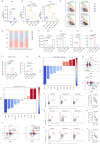
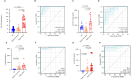
Results: This study identified a subset of CD10-CD121b+ neutrophils in the peripheral blood of patients with septic shock. These patients exhibited elevated concentrations of soluble CD121b in serum and urine. Furthermore, outcomes revealed that the presence of CD121b+ neutrophils positively correlated with the severity of septic shock. These cells displayed immunosuppressive characteristics; after blocking CD121b, proinflammatory cytokines increased in peripheral immune cells. Additionally, we found that treatment with ATRA down-regulated the expression of CD121b.
Conclusions: CD121b is closely associated with the progression of septic shock and may serve as a potential predictor indicator of immunosuppression for the condition.
Keywords: CD121b; cytokine; immunosuppression; neutrophils; septic shock.
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Zhang, Chen, Qin, Hu, Xi, Zhang, Zhou, Zhou, Fu and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of CD177 as the most dysregulated parameter in a microarray study of purified neutrophils from septic shock patients.Immunol Lett. 2016 Oct;178:122-30. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2016.08.011. Epub 2016 Aug 26. Immunol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27568821
-
Source of Circulating Pentraxin 3 in Septic Shock Patients.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 4;9:3048. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03048. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30687307 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor pathway signaling is differently regulated in neutrophils and peripheral mononuclear cells of patients with sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock.Crit Care Med. 2009 Jan;37(1):132-9. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e318192fbaf. Crit Care Med. 2009. PMID: 19050613
-
Epigenetic biomarkers for human sepsis and septic shock: insights from immunosuppression.Epigenomics. 2020 Apr;12(7):617-646. doi: 10.2217/epi-2019-0329. Epub 2020 May 12. Epigenomics. 2020. PMID: 32396480 Review.
-
Neutrophil Activation During Septic Shock.Shock. 2018 Apr;49(4):371-384. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000980. Shock. 2018. PMID: 28858142 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

