Tracking the evolution of serum antibody levels and influencing factors post-SARS-CoV-2 infection among community residents in Fuzhou City
- PMID: 40230855
- PMCID: PMC11994895
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1533102
Tracking the evolution of serum antibody levels and influencing factors post-SARS-CoV-2 infection among community residents in Fuzhou City
Abstract
Objective: To track the level of serum antibodies in Fuzhou residents and analyze the possible influencing factors of serum antibodies, so as to provide a scientific basis for the adjustment of population immunity and prevention and control strategies.
Methods: Residents in the Fuzhou community who had symptoms of covid-19 infection or who had tested positive for nucleic acid or antigen since December 2022 were selected for the questionnaire survey and their sera were collected to analyze the trend of antibody changes, the antibody level was divided into high antibody group and low antibody group according to the literature data. The possible influencing factors of serum antibody level was analyzed by multivariate logistic regression model.
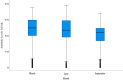
Results: A total of 2,521 Fuzhou residents were adopted in the study, including 223 in the high antibody group and 194 in the low antibody group. A univariate analysis showed that, there were significant differences in age (Z=-4.028, P<0.00), occupation (χ2 = 18.591, P=0.005), typical symptoms after the first infection (χ2 = 9.784, P=0.002), history of surgery (χ2 = 29.542, P<0.001), symptoms lasting more than 2 weeks after the first infection (χ2 = 4.887, P=0.027), smoking (χ2 = 18.524, P<0.001) and drinking (χ2 = 19.578, P<0.001) between the high antibody group and the low antibody group. Multivariate regression models show that, age (OR= 1.011, 95%CI: 1.002~1.020, P=0.017), history of surgery (OR=4.956,95%CI: 2.606~9.423, P<0.001),smoking (OR=2.089, 95%CI: 1.002~4.355, P=0.049), drinking (OR=2.214, 95%CI: 1.066~4.600, P=0.033) were the risk factors affecting antibody level. Typical symptoms after the first infection (OR=0.224, 95%CI: 0.086~0.579, P=0.002) and symptoms lasting more than 2 weeks after the first infection (OR=0.432, 95%CI: 0.258~0.723, P=0.001) were protective factors. By observing the trend of antibody changes in 3, 6 and 9 months, we found that the level of IgG antibody showed a decreasing trend.
Conclusions: The high level of protection was more likely to occur in young adults, people without operation history, people without smoking history, people without drinking history, people with typical symptoms after the first infection and symptoms lasting more than 2 weeks after the first infection. The level of IgG antibody was decreased in general, so it is necessary to strengthen immunization.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; community residents; influencing factors; logistic regression; serum antibody.
Copyright © 2025 Zheng, Chen, Liao and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Seroconversion and dynamics of IgG anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies during the pandemic: A two-month observation cohort study on the population of Sleman in Indonesia.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 2;20(1):e0316360. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316360. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39746050 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 seropositivity and subsequent infection risk in healthy young adults: a prospective cohort study.Lancet Respir Med. 2021 Jul;9(7):712-720. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00158-2. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Lancet Respir Med. 2021. PMID: 33865504 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence and humoral immune durability of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in Wuhan, China: a longitudinal, population-level, cross-sectional study.Lancet. 2021 Mar 20;397(10279):1075-1084. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00238-5. Lancet. 2021. PMID: 33743869 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 Specific and Neutralizing Antibodies over Seven Months after Symptom Onset in COVID-19 Patients.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0059021. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00590-21. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34550000 Free PMC article.
-
Factors influencing antibody response after COVID-19 recombinant protein vaccination in adults: A cross-sectional observational study, in Chongqing, China.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2389602. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2389602. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 39171541 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous