Small extracellular vesicle miRNAs as biomarkers for predicting antitumor efficacy in lung adenocarcinoma treated with chemotherapy and checkpoint blockade
- PMID: 40230863
- PMCID: PMC11994727
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1573043
Small extracellular vesicle miRNAs as biomarkers for predicting antitumor efficacy in lung adenocarcinoma treated with chemotherapy and checkpoint blockade
Abstract
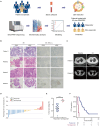
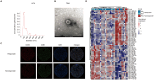
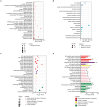
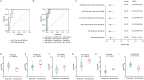
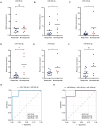
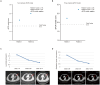
Checkpoint blockade combined with chemotherapy has become an important treatment option for lung cancer patients in clinical settings. However, biomarkers that effectively identify true responders remain lacking. We assessed the potential of plasma small extracellular vesicle (sEV)-derived microRNAs (miRNAs) as biomarkers for predicting and identifying responders to combined immunochemotherapy. A total of 29 patients with lung adenocarcinoma who received pembrolizumab combined with pemetrexed and carboplatin were enrolled. The efficacy evaluation revealed that 24 patients obtained durable clinical benefits from combined immunochemotherapy, and the rest experienced disease progression. Using unsupervised hierarchical clustering, 56 differentially expressed miRNAs (DEMs) were identified between responders and nonresponders. Efficacy prediction models incorporating a combination of sEV miRNAs were established and showed good performance (area under the curve (AUC) > 0.9). In addition, we found that miR-96-5p and miR-6815-5p were notably downregulated in the nonresponder group, while miR-99b-3p, miR-100-5p, miR-193a-5p, and miR-320d were upregulated. These findings were further confirmed by clinical imaging. sEV miRNAs derived from patients with lung cancer showed promise for identifying true responders to combined immunochemotherapy.
Keywords: chemotherapy; immune checkpoint inhibitors; lung cancer. sEV miRNAs predicting immunochemotherapy efficacy; miRNA; sEVs.
Copyright © 2025 Sun, Zhang, Zhang, Yu, Hu, Xu, Zhao, Chen, Zhang, Nian, Lin, Li, Wu, Yu, Wu, Wang, Hui, Zhang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
FZ, JZ, XX, SC, BN, ZL, and DZ are affiliated with 3D Medicines Inc. and are current or former employees. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

