Role of hsa_Circ_0001821 in Colorectal Cancer Pathogenesis and Response to 5-Fluorouracil through miR-203a-3p/FGF-2 Axis
- PMID: 40231340
- PMCID: PMC12040633
- DOI: 10.61186/ibj.4942
Role of hsa_Circ_0001821 in Colorectal Cancer Pathogenesis and Response to 5-Fluorouracil through miR-203a-3p/FGF-2 Axis
Abstract
Background: Chemoresistance, the primary cause of disease relapse and treatment failure, poses a significant challenge in the treatment of colorectal cancer (CRC). Understanding the molecular mechanisms that underlie the pathogenesis and chemoresistance of colorectal tumor cells, as well as identifying novel therapeutic strategies, would be crucial. This study aimed to evaluate the role of hsa_Circ_0001821 in response to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) in CRC, a topic that has not been examined to date.
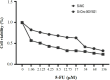
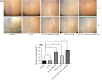
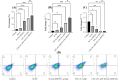
Methods: The current study investigated the effect of hsa_Circ_0001821 suppression using interfering RNAs on the response of colorectal tumor cells to 5-FU. The expression levels of hsa_Circ_0001821, hsa-miR-203a-3p, BAX, BCL-2, and FGF-2 were determined via quantitative RT-PCR. Cell survival, migration rate, and apoptosis induction of colorectal tumor cells subjected to 5-FU treatment were assessed using the MTT test, scratch assay, and flow cytometry analysis, respectively.
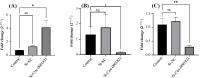
Results: Knockdown of hsa_Circ_0001821 with siRNA increased the expression level of hsa-miR-203a-3p and decreased the expression level of FGF-2. Additionally, the knockdown of hsa_Circ_0001821 enhanced the sensitivity of colorectal tumor cells to 5-FU. This circRNA significantly affected the viability, apoptosis, and migration of tumor cells.
Conclusion: Our study reveals the potential role of hsa_Circ_0001821 in controlling the tumor cell viability and response to 5-FU by targeting the hsa-miR-203a-3p/FGF-2 axis. These findings enhance our understanding of the molecular mechanisms that influence chemotherapy response in CRC, paving the way for the identification of more effective treatments for this disease.
Keywords: Antineoplastic Agents; Circular RNA; Colorectal Neoplasm; MicroRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exosome-Mediated Transfer of circ_0000338 Enhances 5-Fluorouracil Resistance in Colorectal Cancer through Regulating MicroRNA 217 (miR-217) and miR-485-3p.Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Apr 22;41(5):e00517-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00517-20. Print 2021 Apr 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33722958 Free PMC article.
-
Homo Sapiens Circular RNA 0079993 (hsa_circ_0079993) of the POLR2J4 Gene Acts as an Oncogene in Colorectal Cancer Through the microRNA-203a-3p.1 and CREB1 Axis.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Sep 13;25:6872-6883. doi: 10.12659/MSM.916064. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31515467 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0004650 Enhances 5-Fluorouracil Resistance in Gastric Cancer via Sponging miR-145-5p.Anticancer Res. 2024 Dec 30;45(1):173-187. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.17403. Anticancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39740828
-
Hsa_circ_0087862 contributes to the progression of colorectal cancer through regulating miR-512-3p/HK2 axis.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 May;257:155281. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155281. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38669868
-
Circ_0070934 Regulates the Proliferation, Metastasis, and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Colorectal Cancer Cells by Targeting miR-203a-3p/HOXA13 Axis.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025 Feb;39(2):e70173. doi: 10.1002/jbt.70173. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39967473
Cited by
-
Circular RNAs as Targets for Developing Anticancer Therapeutics.Cells. 2025 Jul 18;14(14):1106. doi: 10.3390/cells14141106. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40710359 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sharma V, Chouhan P, Pandey RK, Prajapati VK. Recent therapeutic strategies for the treatment of colon cancer. Colon Cancer Dx Therap. 2021;2:73–90.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
