Accuracy of smartwatches for measuring heart rate and oxygen saturation in cynomolgus macaques compared to clinical standards
- PMID: 40231405
- PMCID: PMC12374010
- DOI: 10.1177/00236772251318910
Accuracy of smartwatches for measuring heart rate and oxygen saturation in cynomolgus macaques compared to clinical standards
Abstract
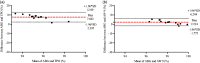
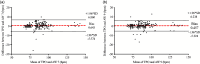
Continuous monitoring of physiological parameters in non-human primates (NHPs) necessitates a precise, non-invasive, and convenient method. This study aimed to validate the use of smartwatches with integrated pulse oximetry and heart rate (HR) monitoring capabilities for use in NHPs. Currently, the clinical standard for non-invasive continuous monitoring of peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) in NHPs has been the use of a transmittance pulse oximeter (TPO) affixed to a location of highly vascularized tissue. In a clinical setting, HR is monitored through electrocardiogram (ECG) or associated with SpO2 measurement from a TPO probe utilizing photoplethysmography technology. Challenges in obtaining precise readings with TPOs stem from technological limitations and probe placement restrictions. To address these limitations, simultaneous HR and SpO2 measurements were obtained from 15 cynomolgus macaques (Macaca fascicularis) using the Apple Watch 7 (AW 7), Apple Watch 9 (AW 9), and a clinical-grade TPO probe with integrated optical HR measurement technology (iM70, ELAN). Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis was used as a reference method for SpO2. We found that a TPO device significantly underestimated SpO2 compared to the AW 7 and AW 9 when referenced against ABG values. Smartwatch-derived HR and SpO2 measurements demonstrated good agreement and minimal bias compared to the gold standard method. Overall, the AW 7 and AW 9 exhibited good agreement with clinical reference standards for HR and good agreement with the gold standard for SaO2 in sedated cynomolgus macaques.
La surveillance continue des paramètres physiologiques chez les primates non-humains (PNH) nécessite une méthode précise, non-invasive et pratique. Cette étude visait à valider l’utilisation de smartwatches avec oxymétrie de pouls intégrée et capacités de surveillance de la fréquence cardiaque (FC) pour une utilisation chez les PNH. Actuellement, la norme clinique de surveillance continue non-invasive de la saturation périphérique en oxygène (SpO2) chez les PNH consiste à utiliser un oxymètre de pouls à transmittance (TPO) fixé dans un emplacement de tissu fortement vascularisé. En milieu clinique, la FC est surveillée par électrocardiogramme (ECG) ou associée à la mesure de la SpO2 à partir d’une sonde d’oxymètre de pouls à transmittance (TPO) utilisant la technologie de photopléthysmographie (PPG). Les difficultés rencontrées pour obtenir des relevés précis avec les TPO découlent de limitations technologiques et de restrictions de placement des sondes. Pour remédier à ces limites, des mesures simultanées de la FC et de la SpO2 ont été obtenues sur 15 singes cynomolgus (Macaca fascicularis) à l’aide de l’Apple Watch 7 (AW 7), de l’Apple Watch 9 (AW 9) et d’une sonde TPO de qualité clinique avec technologie optique intégrée de mesure de la FC (iM70, ELAN). L’analyse des gaz du sang artériel (GSA) a été utilisée comme méthode de référence pour la SpO2. Nous avons constaté qu’un appareil TPO sous-estimait significativement la SpO2 par rapport aux AW 7 et AW 9 par rapport aux valeurs de GSA. Les mesures de FC et SpO2 provenant des smartwatches ont démontré une bonne concordance et un biais minimal par rapport à la méthode de référence. Dans l’ensemble, les AW 7 et AW 9 présentent un bon accord avec les normes de référence cliniques pour la HR et un bon accord avec l’étalon-or pour Sao2 chez les singes cynomolgus sédatés.
Die kontinuierliche Überwachung physiologischer Parameter bei nichtmenschlichen Primaten (NHP) erfordert eine präzise, nichtinvasive und praktische Methode. Ziel dieser Studie war es, die Verwendung von Smartwatches mit integrierter Pulsoximetrie und Herzfrequenzüberwachung für den Einsatz bei NHP zu validieren. Derzeit ist der klinische Standard für die nichtinvasive kontinuierliche Überwachung der peripheren Sauerstoffsättigung (SpO2) bei NHP die Verwendung eines Transmissionspulsoximeters (TPO), das an einer Stelle mit stark vaskularisiertem Gewebe angebracht wird. Im klinischen Umfeld wird die Herzfrequenz mit Hilfe eines Elektrokardiogramms (EKG) oder in Verbindung mit der SpO2-Messung durch eine Transmissionspulsoximetersonde (TPO) unter Verwendung der Photoplethysmographie (PPG)-Technologie überwacht. Die Herausforderungen bei der Erzielung präziser Messwerte mit TPOs ergeben sich aus technischen Beschränkungen und Zwängen bei der Platzierung der Sonde. Um diese Beschränkungen zu überwinden, wurden simultane HR- und SpO2-Messungen bei 15 Cynomolgus-Makaken (Macaca fascicularis) mit der Apple Watch 7 (AW 7), der Apple Watch 9 (AW 9) und einer klinischen TPO-Sonde mit integrierter optischer HR-Messtechnologie (iM70, ELAN) durchgeführt. Die arterielle Blutgasanalyse (ABG) wurde als Referenzmethode für SpO2 verwendet. Wir fanden heraus, dass ein TPO-Gerät den SpO2-Wert im Vergleich zu AW 7 und AW 9 unter Bezugnahme auf die AGB-Werte signifikant unterschätzt. Die von der Smartwatch abgeleiteten HR- und SpO2-Messungen zeigten eine gute Übereinstimmung und eine minimale Verzerrung im Vergleich zur Goldstandardmethode. Insgesamt zeigen AW 7 und AW 9 eine gute Übereinstimmung mit klinischen Referenzstandards für die Herzfrequenz und eine gute Übereinstimmung mit dem Goldstandard für SaO2 bei sedierten Cynomolgus-Makaken.
La monitorización continua de los parámetros fisiológicos en primates no humanos (PNH) requiere un método preciso, no invasivo y cómodo. Este estudio pretendía validar el uso de relojes inteligentes con capacidades integradas de monitorización de la pulsioximetría y la frecuencia cardiaca (FC) para su uso en PNH. En la actualidad, el estándar clínico para la monitorización continua no invasiva de la saturación periférica de oxígeno (SpO2) en los PNH ha sido el uso de un pulsioxímetro de transmitancia (POT) fijado en un lugar de tejido altamente vascularizado. En un entorno clínico, la FC se monitoriza a través del electrocardiograma (ECG) o asociada a la medición de la SpO2 a partir de una sonda de pulsioximetría de transmitancia (POT) que utiliza la tecnología de la fotopletismografía (FPG). Los retos a la hora de obtener lecturas precisas con los POT se derivan de las limitaciones tecnológicas y de las restricciones en la colocación de las sondas. Para abordar estas limitaciones, se obtuvieron mediciones simultáneas de la FC y la SpO2 de 15 macacos cynomolgus (Macaca fascicularis) utilizando el Apple Watch 7 (AW 7), el Apple Watch 9 (AW 9) y una sonda POT de grado clínico con tecnología de medición óptica de la FC integrada (iM70, ELAN). Se utilizó el análisis de gases en sangre arterial (GSA) como método de referencia para la Spo2. Descubrimos que el dispositivo POT subestimaba significativamente la SpO2 en comparación con el AW 7 y el AW 9 cuando se comparaba con los valores GSA. Las mediciones de FC y SpO2 derivadas del reloj inteligente demostraron una buena concordancia y un sesgo mínimo en comparación con el método de referencia. En general, los modelos AW 7 y AW 9 muestran una buena concordancia con los estándares de referencia clínicos para la frecuencia cardíaca (HR) y una buena concordancia con el estándar de referencia para la SaO2 en macacos cínomolgus sedados.
Keywords: Monitoring; anesthesia; macaques; techniques; technology.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Validity of pulse oximetry measures for heart rate and oxygen saturation during profound hypoxia in normobaric simulated extreme altitudes.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 23;20(6):e0326674. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326674. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40549783 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of non-invasive oxygen reserve index versus standard SpO2 monitoring on peripheral oxygen saturation during endotracheal intubation in the intensive care unit: Protocol for the randomized controlled trial NESOI2.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 16;19(9):e0307723. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307723. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39283873 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Fetal pulse oximetry for fetal assessment in labour.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Oct 7;2014(10):CD004075. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004075.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25287809 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of targeting lower versus higher arterial oxygen saturations on death or disability in preterm infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 11;4(4):CD011190. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011190.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28398697 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith JC, Danneman PJ. Anesthesia and Analgesia in Laboratory Animals. 2nd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2008.
-
- Young SS, Skeans SM, Lamca JE, et al. Agreement of SpO2, SaO2 and ScO2 in anesthetized cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). Vet Anaesth Analg 2002; 29: 150–155. - PubMed
-
- Yanmaz LE, Okur S, Ersoz U, et al. Two different smartwatches exhibit high accuracy in evaluating heart rate and peripheral oxygen saturation in cats when compared with the electrocardiography and transmittance pulse oximetry. J Am Vet Med Assoc 2023; 261: 205–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

