Pan-cancer multi-omics analysis to identify the potential pro-oncogenic properties of GREM1 as a promising targets for cancer prognosis and therapeutics
- PMID: 40231657
- PMCID: PMC12033649
- DOI: 10.1177/03946320251331850
Pan-cancer multi-omics analysis to identify the potential pro-oncogenic properties of GREM1 as a promising targets for cancer prognosis and therapeutics
Abstract
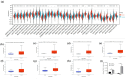
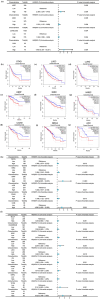
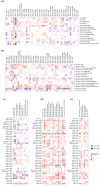
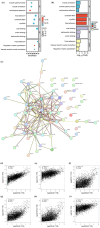
We aimed to investigate the potential pro-oncogenic properties of GREM1 by Pan-cancer multi-omics analysis. Accumulating evidence has highlighted that GREM1 (Gremlin 1), serves as an inhibitor of BMP (Bone Morphogenetic Protein) family, involve in bone related diseases, carcinogenesis, cell stemness, and cell differentiation. However, the effect and underlying mechanism of GREM1 on the cancer biology remain largely elusive. The mRNA expression of GREM1 were extracted from GTEx (Genotype-Tissue Expression) and TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas) database. Analysis of OS (Overall Survival), PFI (Progression Free Interval), DSS (Disease-Specific Survival), and ROC (Receiver Operating Characteristic) were performed to predicted prognostic value of GREM1 in various cancers. The TIMER (Tumor Immune Estimation Resource) online tool was used to investigate the relationship between GREM1 transcriptional level and infiltration of immune cells. KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) analysis and GO (Gene Ontology) analysis were used to investigate the GREM1 related molecular events, and then constructed a PPI (Protein-Protein Interaction) network via the STRING (Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interaction Genes/Proteins) online tool. Western blot was performed to investigate the indicated protein expression. In the present study, our results showed that GREM1 tended to be upregulated in various cancers, which would correlate with the poor prognosis. Mechanistically, our results showed that GREM1 involve in regulating the ECM-receptor interaction pathway, upregulation of MMP activity, angiogenesis, and immune cell infiltration. In vitro studies, our results further showed that BMP agonist significantly decreased the protein level of GREM1 in GES-1 cells and BGC cells, which accompanied by inhibiting migration and proliferation in GES-1 cells and BGC cells. BMP inhibitor significantly promoted GREM1 expression and migration in BGC cells, but not GES-1 cells. GREM1 might serve as a potential and promising prognostic biomarker for drug development and cancer treatment.
Keywords: Gremlin 1; migration; pan-cancer; prognosis; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
UBR1 is a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target associated with immune cell infiltration in gastric cancer.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Aug 23;16(16):12029-12049. doi: 10.18632/aging.206079. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 39181686 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive prognostic and immunological implications of Gremlin 1 in lung adenocarcinoma.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 24;16:1529195. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1529195. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40066442 Free PMC article.
-
Gremlin-1: An endogenous BMP antagonist induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and interferes with redifferentiation in fetal RPE cells with repeated wounds.Mol Vis. 2019 Oct 21;25:625-635. eCollection 2019. Mol Vis. 2019. PMID: 31700227 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into Gremlin-1: A tumour microenvironment landscape re-engineer and potential therapeutic target.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2025 Jun;1872(5):119962. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2025.119962. Epub 2025 Apr 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2025. PMID: 40250712 Review.
-
The Role of GREMLIN1, a Bone Morphogenetic Protein Antagonist, in Cancer Stem Cell Regulation.Cells. 2025 Apr 11;14(8):578. doi: 10.3390/cells14080578. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40277903 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The functional and clinical significance of nucleoporin NUP153 across human cancers: a systematic study based on multi-omics analysis and bench work validation.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 18;16:1613688. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1613688. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40607419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, et al.. (2023) Cancer statistics. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 73(1): 17–48. - PubMed
-
- Jin Z, Cao Y. (2024) Gremlin1: A BMP antagonist with therapeutic potential in oncology. Investigational New Drugs 42(6): 716–727. - PubMed
-
- Lan L, Evan T, Li H, et al.. (2022) GREM1 is required to maintain cellular heterogeneity in pancreatic cancer. Nature 607(7917): 163–168. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

