In Vivo pharmacokinetic interactions of ribociclib with rivaroxaban and apixaban in rats: implications for increased drug exposure and dose adjustments
- PMID: 40231674
- PMCID: PMC11994961
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1530806
In Vivo pharmacokinetic interactions of ribociclib with rivaroxaban and apixaban in rats: implications for increased drug exposure and dose adjustments
Abstract
Background: Apixaban (API) and rivaroxaban (RIVA) are orally available inhibitors of coagulation factor Xa and are commonly used to treat cancer-related venous thrombosis. Ribociclib (RIBO), a first-line treatment for hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 negative (HR+/HER2-) advanced breast cancer, is an inhibitor of CYP3A4, P-gp, and BCRP. Given the potential for these drugs to be co-administered in clinical settings, there is limited information regarding the pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions (DDIs) between ribociclib and these anticoagulants. This study aimed to evaluate the extent of DDIs between ribociclib and rivaroxaban or apixaban in rats and to explore the optimization of drug dosing strategies.
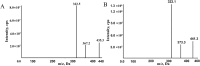
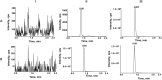
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into 9 groups (n = 6), receiving ribociclib, apixaban, rivaroxaban, ribociclib with rivaroxaban, ribociclib with apixaban, and combinations with reduced doses and time intervals. Blood concentrations were measured using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). Pharmacokinetic parameters such as AUC, Cmax, CLz/F, and Vz/F.
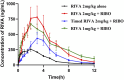
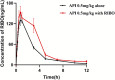
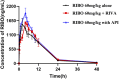
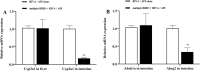
Results: Ribociclib significantly increased exposure to both rivaroxaban and apixaban, with a greater impact on rivaroxaban. Specifically, ribociclib increased the AUC0-t, AUC0-∞ and Cmax of rivaroxaban (normal dose) by about 2.4-fold, 2.1-fold and 1.8-fold, while increasing apixaban exposure by about 60.82%, with a trend towards an increase in Cmax that was not statistically significant. When co-administered with ribociclib, even at a reduced dosage of 1 mg/kg, rivaroxaban exhibited a significant increase in exposure, with the AUC increasing by 2.3-fold and Cmax by 1.3-fold. Despite the reduction in dosage, the pharmacokinetic effect of ribociclib on rivaroxaban persisted. While administration of rivaroxaban 12 h after ribociclib resulted in a less pronounced increase in exposure compared to the normal-dose group. The results of qRT-PCR showed that ribociclib reduced the expression of Cyp3a1 and Abcg2 in rat intestine.
Discussion: This research highlights the need for careful consideration of dosing regimens to minimize toxicity risk and optimize the safety of clinical co-administration of ribociclib with rivaroxaban.
Keywords: apixaban; cancer-associated venous thromboembolism; drug-drug interaction; ribociclib; rivaroxaban.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Du, Wang, Wang, An, Ma, Dong and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vivo evaluation of the pharmacokinetic interactions between almonertinib and rivaroxaban, almonertinib and apixaban.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 4;14:1263975. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1263975. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37860116 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of furmonertinib on the pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban or apixaban in vivo.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2025 Jan 15;1251:124425. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2024.124425. Epub 2024 Dec 10. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39675152
-
Predicting drug-drug interactions with physiologically based pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modelling and optimal dosing of apixaban and rivaroxaban with dronedarone co-administration.Thromb Res. 2022 Oct;218:24-34. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2022.08.007. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Thromb Res. 2022. PMID: 35985100
-
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic drug interactions with new oral anticoagulants: what do they mean for patients with atrial fibrillation?Ann Pharmacother. 2013 Nov;47(11):1478-87. doi: 10.1177/1060028013504741. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Ann Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 24259602 Review.
-
Anticoagulant therapy with the oral direct factor Xa inhibitors rivaroxaban, apixaban and edoxaban and the thrombin inhibitor dabigatran etexilate in patients with hepatic impairment.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013 Apr;52(4):243-54. doi: 10.1007/s40262-013-0034-0. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013. PMID: 23389892 Review.
References
-
- Amin A., Naeem M. O., Amin L., Khaliq S. U., Ahmad A., Vohra R. R., et al. (2024). Apixaban versus low molecular weight heparin in patients with cancer-associated venous thromboembolism: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Med. Surg. 86 (8), 4675–4683. 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002147 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bellesoeur A., Thomas-Schoemann A., Allard M., Smadja D., Vidal M., Alexandre J., et al. (2018). Pharmacokinetic variability of anticoagulants in patients with cancer-associated thrombosis: clinical consequences. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 129, 102–112. 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2018.06.015 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

