Root restriction accelerates genomic target identification in quinoa under controlled conditions
- PMID: 40231839
- PMCID: PMC11998636
- DOI: 10.1111/ppl.70223
Root restriction accelerates genomic target identification in quinoa under controlled conditions
Abstract
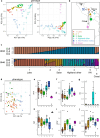
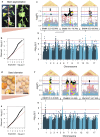
Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) is a nutritious and resilient crop that displays a high genetic and phenotypic variation. As the popularity of this crop increases, there is a growing need to integrate classic and modern breeding tools to favor its improvement. We tested root restriction as a method to reduce plant size and enable high-throughput phenotypic screening of large sets of quinoa plants under controlled conditions. We verified how increasing root restriction does not affect the prediction of field behavior with respect to other standard greenhouse cultivation procedures. We then combined the phenotypic information obtained with our root restriction system with whole-genome re-sequencing data to characterize a quinoa diversity panel of 100 accessions and showed that phenotypic data obtained from root-restricted plants provide real insights into quinoa genetics. Finally, we carried out a genome-wide association study (GWAS) and identified a previously described locus for betalain biosynthesis, as well as other candidate loci linked to betalain biosynthesis and seed size. Overall, we showed that a phenotyping system based on root restriction can aid the identification of genomic targets in quinoa, which can complement and inform field trials for certain traits. This work supports further breeding and faster improvement of quinoa.
© 2025 The Author(s). Physiologia Plantarum published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Scandinavian Plant Physiology Society.
Figures

References
-
- Aguilar, P. C. , & Jacobsen, S.‐E. (2003). Cultivation of quinoa on the Peruvian altiplano. Food Reviews International, 19(1–2), 31–41. 10.1081/FRI-120018866 - DOI
-
- Al‐Naggar, A. M. M. , El‐Salam, R. M. A. , Badran, A. E. E. , & El‐Moghazi, M. M. A. (2017). Heritability and interrelationships for agronomic, physiological and yield traits of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) under elevated water stress. Archives of Current Research International, 10(3), 1–15. 10.9734/ACRI/2017/37215 - DOI
-
- Asseng, S. , Ewert, F. , Martre, P. , Rötter, R. P. , Lobell, D. B. , Cammarano, D. , Kimball, B. A. , Ottman, M. J. , Wall, G. W. , White, J. W. , Reynolds, M. P. , Alderman, P. D. , Prasad, P. V. V. , Aggarwal, P. K. , Anothai, J. , Basso, B. , Biernath, C. , Challinor, A. J. , De Sanctis, G. , … Zhu, Y. (2015). Rising temperatures reduce global wheat production. Nature Climate Change, 5(2), Article 2. 10.1038/nclimate2470 - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

