Effect of Canthaxanthin on Egg Yolk Quality of Huaixiang Laying Hens at Normal and High Temperature
- PMID: 40231966
- PMCID: PMC11941421
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14060950
Effect of Canthaxanthin on Egg Yolk Quality of Huaixiang Laying Hens at Normal and High Temperature
Abstract
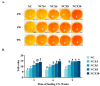
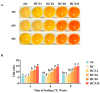
(1) Background: Thermal stress in Guangdong's tropical/subtropical regions significantly compromises yolk quality in Huaixiang chickens. Canthaxanthin (CX), an effective feed additive, has been demonstrated to not only enhance the nutritional composition of egg yolks but also mitigate heat stress. This study systematically evaluates the effects of dietary CX supplementation on egg production rate and yolk nutritional components (e.g., amino acids, lipids, vitamin B2) in Huaixiang hens under both normal and high-temperature environments. (2) Methods: A factorial design was implemented, exposing hens to either thermoneutral (25 ± 2 °C, 65-75% RH) or high-temperature (32 ± 2 °C, 65-75% RH) conditions. Diets were supplemented with graded CX levels (0, 4, 6, 8, or 10 mg/kg) for 9 weeks. Laying performance and yolk nutritional profiles (amino acids, lipids, minerals, vitamin B2) were evaluated at 3-week intervals (3rd, 6th, and 9th weeks. (3) Results: Under normal temperature conditions, the addition of CX significantly enhanced the laying rate, relative yolk weight, yolk color score, lecithin (LEC) content, and it optimized the amino acid profile of the yolk. Under high-temperature conditions, the laying rate, yolk weight, yolk weight ratio, total amino acid content, yolk triglyceride (TG), LEC, and vitamin B2 (VB2) levels in Huaixiang chickens all decreased. However, supplementation with CX under high-temperature conditions effectively mitigated these adverse effects: the laying rate was restored to levels observed under normal temperature conditions, while the relative yolk weight, color score, TG, total cholesterol (TC), LEC, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), calcium (Ca), and VB2 levels were significantly higher than those in the heat-stressed control group. Additionally, the amino acid composition of the yolk was improved. (4) Conclusion: CX enhances the nutrient content of egg yolks under both normal and high-temperature conditions, providing a valuable reference for the production of healthy and high-quality eggs.
Keywords: canthaxanthin; egg yolk quality; high temperature; laying hens; poultry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dietary Canthaxanthin Supplementation Promotes the Laying Rate and Follicular Development of Huaixiang Hens.Biology (Basel). 2023 Oct 27;12(11):1375. doi: 10.3390/biology12111375. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37997976 Free PMC article.
-
Effects and Mechanisms Investigation of Heat Stress on Egg Yolk Quality in Huaixiang Chickens.Animals (Basel). 2023 Nov 14;13(22):3513. doi: 10.3390/ani13223513. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38003131 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary supplementation of spirulina and canthaxanthin boosts laying performance, lipid profile in blood and egg yolk, hatchability, and semen quality of chickens.J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2023 Mar;107(2):650-658. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13729. Epub 2022 May 9. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2023. PMID: 35534942
-
Effect of dietary canthaxanthin and iodine on the production performance and egg quality of laying hens.Poult Sci. 2018 Nov 1;97(11):4008-4019. doi: 10.3382/ps/pey264. Poult Sci. 2018. PMID: 29931093
-
Effects of vitamin E supplementation on performance, serum biochemical parameters and fatty acid composition of egg yolk in laying hens fed a diet containing ageing corn.J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2019 Jan;103(1):135-145. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13017. Epub 2018 Oct 27. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30368939
References
-
- Gheller B.J., Blum J.E., Lim E.W., Handzlik M.K., Hannah Fong E.H., Ko A.C., Khanna S., Gheller M.E., Bender E.L., Alexander M.S., et al. Extracellular Serine and Glycine Are Required for Mouse and Human Skeletal Muscle Stem and Progenitor Cell Function. Mol. Metab. 2021;43:101106. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Robert C., Buisson C., Laugerette F., Abrous H., Rainteau D., Humbert L., Vande Weghe J., Meugnier E., Loizon E., Caillet F., et al. Impact of Rapeseed and Soy Lecithin on Postprandial Lipid Metabolism, Bile Acid Profile, and Gut Bacteria in Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021;65:e2001068. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202001068. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Herranz B., Romero C., Sánchez-Román I., López-Torres M., Viveros A., Arija I., Álvarez M.D., de Pascual-Teresa S., Chamorro S. Enriching Eggs with Bioactive Compounds through the Inclusion of Grape Pomace in Laying Hens Diet: Effect on Internal and External Egg Quality Parameters. Foods. 2024;13:1553. doi: 10.3390/foods13101553. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

