Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation Reveal Therapeutic Potential of Propolis in UV-Induced Allergic Dermatitis
- PMID: 40232010
- PMCID: PMC11941912
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14060996
Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation Reveal Therapeutic Potential of Propolis in UV-Induced Allergic Dermatitis
Abstract
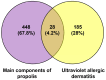
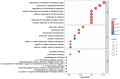
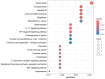
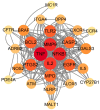
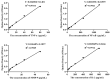
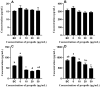
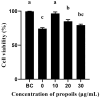
Propolis demonstrates diverse pharmacological properties encompassing antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and wound-healing activities. This study investigated the therapeutic mechanism of propolis against ultraviolet (UV)-induced allergic dermatitis through an integrated approach combining network pharmacology with in vitro experimental validation. The targets of propolis components were conducted through the PubChem, the EMBL-EBI, and SEA Search Server databases, and the disease-associated targets for atopic dermatitis and related allergic conditions were extracted from GeneCards. The overlapping targets between propolis components and UV-induced dermatitis were screened. The Gene Ontology (GO) Enrichment analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis were performed. The key targets were further validated through ELISA experiments using HSF cells. The results show that there were 28 overlapping targets between propolis and UV-induced allergic dermatitis. The GO enrichment results show that there were 1246 terms of biological functions, 52 terms of cellular components, and 98 terms of molecular functions. KEGG pathway enrichment obtained 110 signaling pathways. The protein-protein interaction (PPI) network showed that TNF, NFKB1, MMP-9, and IL-2 were hub proteins. The ELISA experiment confirmed that propolis reduced the levels of MMP-9 and IL-2 in UBV-induced allergic dermatitis of HSF cells in a dose-dependent manner. These findings provide mechanistic evidence supporting propolis as a promising functional food, dietary supplements, or medicinal agent for UV-induced allergic skin disorders.
Keywords: UV-induced allergic dermatitis; in vitro; network pharmacology; propolis; treatment strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking and Experimental Verification Revealing the Mechanism of Fule Cream against Childhood Atopic Dermatitis.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024;20(6):860-875. doi: 10.2174/0115734099257922230925074407. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024. PMID: 37807411
-
Based on network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental verification to reveal the mechanism of Andrographis paniculata against solar dermatitis.Phytomedicine. 2024 Dec;135:156025. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156025. Epub 2024 Sep 7. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39326136
-
Mechanisms of the Compound of Magnoliae Flos and Xanthii Fructus Essential Oils for the Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis based on the Integration of Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Animal Experiment.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025 Jan 22. doi: 10.2174/0113862073333657241216040227. Online ahead of print. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025. PMID: 39844421
-
Network pharmacology integrated with experimental validation reveals the mechanism of Xanthii Fructus against allergic rhinitis via JAK2/STAT3/HIF-1α signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Mar 13;343:119461. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119461. Epub 2025 Feb 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39923957
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
References
-
- Verma A., Zanoletti A., Kareem K.Y., Adelodun B., Kumar P., Ajibade F.O., Silva L.F.O., Phillips A.J., Kartheeswaran T., Bontempi E., et al. Skin protection from solar ultraviolet radiation using natural compounds: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024;22:273–295. doi: 10.1007/s10311-023-01649-4. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

