The Pomegranate Flower Water Extract Negatively Regulates Melanogenesis by Suppressing MITF Expression and Its Target Enzymes
- PMID: 40232012
- PMCID: PMC11998895
- DOI: 10.1111/jocd.70163
The Pomegranate Flower Water Extract Negatively Regulates Melanogenesis by Suppressing MITF Expression and Its Target Enzymes
Abstract
Background: The aesthetic issues caused by pigmentation are increasing people's demand for skin whitening. Considering its long-term use, it is very important for searching safe and effective agents. Pomegranate flower, a kind of traditional Chinese medicine, has shown promising anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antidiabetic properties, but its potential skin-lightening effects have not been well explored.
Aims: We investigated the effect of pomegranate flower water extract (PFE) on skin lightening and elucidated its underlying mechanisms.
Methods: The radical scavenging capacity was measured by ABTS and DPPH assays, and the mechanism of lightening was detected by Western blot.
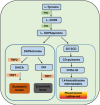
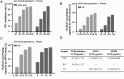
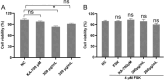
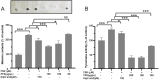
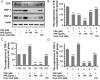
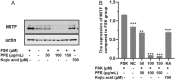
Results: PFE could obviously inhibit tyrosinase activity, which its inhibition IC50 value was lower than the positive control, kojic acid. Meanwhile, the radical scavenging capacity was also better than vitamin C (VC). Then the synthesis ability of melanin was measured in B16F10 cells; we found that PFE, in its safe concentrations, could reduce the synthesis of melanin resulting from inhibiting TYR activities. The expression of the main melanogenesis enzymes TYR, TRP-1, and TRP-2 was sharply reduced. Interestingly, MITF, a transcription factor of TYR, was obviously decreased its expression when treated with PFE at 50, 100, and 150 μg/mL, which was even significantly lower than the downregulation by kojic acid.
Conclusion: Pomegranate flower extract possessed a strong antimelanogenesis effect, which resulted from inhibiting the expression of MITF and its downstream target enzymes involved in melanin synthesis. These findings provide a strong scientific basis for the use of PFE as a safe and effective skin-lightening ingredient in the cosmetic industry.
Keywords: antimelanogenesis; cosmetic; melanin; pomegranate flower water extract; tyrosinase activity.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cox C. and Khosrotehrani K., “Pigment Disorders,” Australasian Journal of Dermatology 63 (2022): 123–126, 10.1111/ajd.15_13832. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

