Targeting melanocortin 4 receptor to treat sleep-disordered breathing in mice
- PMID: 40232848
- PMCID: PMC12165796
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI177823
Targeting melanocortin 4 receptor to treat sleep-disordered breathing in mice
Abstract
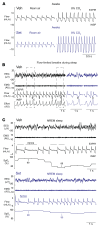
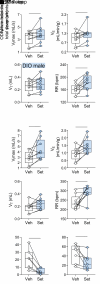
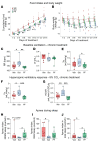
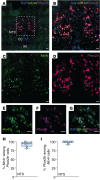
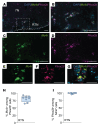
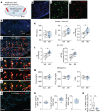
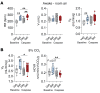
Weight loss medications are emerging candidates for pharmacotherapy of sleep-disordered breathing (SDB). A melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R) agonist, setmelanotide (Set), is used to treat obesity caused by abnormal melanocortin and leptin signaling. We hypothesized that Set can treat SDB in mice with diet-induced obesity. We performed a proof-of-concept randomized crossover trial of a single dose of Set versus vehicle and a 2-week daily Set versus vehicle trial, examined colocalization of Mc4r mRNAs with the markers of CO2-sensing neurons Phox2b and neuromedin B in the brainstem, and expressed Cre-dependent designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drugs (DREADDs) or caspase in obese Mc4r-Cre mice. Set increased minute ventilation across sleep/wake states, enhanced the hypercapnic ventilatory response (HCVR), and abolished apneas during sleep. Phox2b+ neurons in the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) and the parafacial region expressed Mc4r. Chemogenetic stimulation of the MC4R+ neurons in the parafacial region, but not in the NTS, augmented HCVR without any changes in metabolism. Caspase elimination of the parafacial MC4R+ neurons abolished effects of Set on HCVR. Parafacial MC4R+ neurons projected to the respiratory premotor neurons retrogradely labeled from C3-C4. In conclusion, MC4R agonists enhance the HCVR and treat SDB by acting on the parafacial MC4R+ neurons.
Keywords: Mouse models; Neuroscience; Obesity; Pharmacology; Pulmonology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

