Extra virgin olive oil mitigates lung injury in necrotizing enterocolitis: Effects on TGFβ1, Caspase-3, and MDA in a neonatal rat model
- PMID: 40233022
- PMCID: PMC11999148
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320938
Extra virgin olive oil mitigates lung injury in necrotizing enterocolitis: Effects on TGFβ1, Caspase-3, and MDA in a neonatal rat model
Abstract
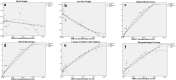
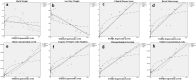
Background: Necrotizing enterocolitis (NE), which is common in premature babies, has been associated with lung damage. Our aim is to explore the effect of enterally administered extra virgin olive oil (EO) with rich polyphenol content on clinical parameters, histopathological score, Transforming growt factor beta-1 (TGFβ1), Caspase 3 and Malondialdehyde (MDA) levels in NE-related lung injury of neonatal rats.
Methods: Three groups (control, NE, NE+EO) were created, with 8 neonatal rats in each group. NE was induced by hypoxia-hyperoxia-hypothermia and formula feeding. EO was given to the treatment group by orogastric probe for 3 days. Intestinal and lung tissue were excised for analysis.
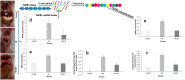
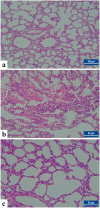
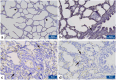
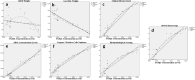
Results: TGFβ1 expression levels, TGFβ1 and MDA concentration levels were higher in the NE compared to NE + EO and control groups (p < 0.001), and their levels decreased after EO treatment compared to the NE group (p < 0.001). It was determined that EO treatment significantly reduced the histopathological damage and the caspase-3 (CASP3) expression level in the lung (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Our findings emphasize that TGFß1 has an crucial function in NE-related lung injury and that EO has therapeutic potential in NE-related lung injury.
Copyright: © 2025 Tuşat et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the protective and therapeutic effects of extra virgin olive oil rich in phenol in experimental model of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis by clinical disease score, ınflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress markers.Pediatr Surg Int. 2024 Mar 17;40(1):80. doi: 10.1007/s00383-024-05669-1. Pediatr Surg Int. 2024. PMID: 38493431
-
Expression of transforming growth factor beta 1 in lung tissue during cardiopulmonary bypass-induced lung injury in dogs.Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013 Dec;61(8):747-53. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1331574. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013. PMID: 23225507
-
Chronic lung injury in the neonatal rat: up-regulation of TGFβ1 and nitration of IGF-R1 by peroxynitrite as likely contributors to impaired alveologenesis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Mar;80:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.12.011. Epub 2014 Dec 13. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25514442
-
Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) for the treatment and prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Oct 28;225:297-308. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.07.009. Epub 2018 Jul 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30005955
-
Ulinastatin Reduces the Severity of Intestinal Damage in the Neonatal Rat Model of Necrotizing Enterocolitis.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Dec 1;25:9123-9130. doi: 10.12659/MSM.919413. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31786582 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exosomal peptides and proteins in wound healing and skin regeneration.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 8. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04426-y. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40627201 Review.
References
-
- Tuşat M, Eroz R, Bölükbaş F, Özkan E, Erdal H. Evaluation of the protective and therapeutic effects of extra virgin olive oil rich in phenol in experimental model of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis by clinical disease score, ınflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress markers. Pediatr Surg Int. 2024;40(1):80. doi: 10.1007/s00383-024-05669-1 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

