The role of ANGPTL4 in cancer: A meta-analysis of observational studies and multi-omics investigation
- PMID: 40233044
- PMCID: PMC11999138
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320343
The role of ANGPTL4 in cancer: A meta-analysis of observational studies and multi-omics investigation
Abstract
Background: Angiopoietin-like protein 4 (ANGPTL4) plays a crucial role in processes such as angiogenesis, inflammation, and metabolism. Despite numerous studies suggesting its involvement in cancer, a definitive role remains unclear. We introduce the first comprehensive meta-analysis and pan-cancer bioinformatics study on ANGPTL4, aiming to unravel its implications across various cancer types.
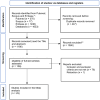
Methods: Moderate-to high-quality observational studies were retrieved from PubMed, Scopus, and Embase. A meta-analysis was conducted using the R package "meta." Survival analysis was performed using GEPIA2 and TIMER2.0. Immune infiltration, mutational burden, and drug resistance analyses was done via GSCAlite. Co-expression and gene set enrichment analyses (GSEA) were carried out using cBioportal and enrichr, respectively.
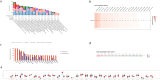
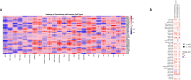
Results: Increased ANGPTL4 expression was linked to worse tumor grade (OR = 1.51, P = 0.023), stage (OR = 2.42, P < 0.001), lymph node metastasis (OR = 1.76, P = 0.012), vascular invasion (OR = 2.16, P = 0.01), and lymphatic invasion (OR = 2.20, P < 0.001). Furthermore, ANGPTL4 expression was linked to worse OS (HR = 1.40, 95% CI: 1.29,1.50, P = 0.0001). Single gene level analysis revealed that ANGPTL4 upregulated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in 23 different cancers. Immune infiltration varied between cancer types, but increased infiltration of cancer-associated fibroblasts was observed in most cancers. Mutation analysis revealed increased alterations in TP53 and CDKN2A in cohorts with ANGPTL4 alterations. GSEA of co-expressed genes revealed involvement in hypoxia, EMT, VEGF-A complex, TGF-B pathways, and extracellular matrix organization.
Conclusions: ANGPTL4 plays a significant role in tumor progression via its positive regulation of EMT and angiogenesis, while possibly harboring a TGF-B dependent role in systemic metastasis. Therefore, ANGPTL4 is a suitable target for future drug development.
Copyright: © 2025 Younis et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal's policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: Anwaar Saeed reports advisory board role with AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Exelixis, Pfizer, Xilio therapeutics, Taiho, Amgen, Autem therapeutics, KAHR medical, and Daiichi Sankyo; institutional research funding from AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Clovis, Exelixis, Actuate therapeutics, Incyte Corporation, Daiichi Sankyo, Five prime therapeutics, Amgen, Innovent biologics, Dragonfly therapeutics, Oxford Biotherapeutics, Arcus therapeutics, and KAHR medical; and participation as a data safety monitoring board chair for Arcus therapeutics. The remaining authors have no relevant financial interests to disclose. This paper has not received funding from any organization.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Transcriptome-wide analysis reveals potential roles of CFD and ANGPTL4 in fibroblasts regulating B cell lineage for extracellular matrix-driven clustering and novel avenues for immunotherapy in breast cancer.Mol Med. 2025 May 8;31(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01237-y. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40340806 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of angiopoietin‑like 4 in human tumors (Review).Int J Oncol. 2025 Feb;66(2):9. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5715. Epub 2024 Dec 20. Int J Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39704206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomic and functional analysis of ANGPTL4 overexpression in pancreatic cancer nominates targets that reverse chemoresistance.BMC Cancer. 2023 Jun 8;23(1):524. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11010-1. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37291514 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role of ANGPTL4 in cancer progression, metastasis, and metabolism: a brief review.BMB Rep. 2024 Aug;57(8):343-351. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2024-0082. BMB Rep. 2024. PMID: 39044455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum Angiopoietin-Like Protein 4: A Potential Prognostic Biomarker for Prediction of Vascular Invasion and Lymph Node Metastasis in Cholangiocarcinoma Patients.Front Public Health. 2022 Mar 22;10:836985. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.836985. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35392474 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

