A drug that induces the microRNA miR-124 enables differentiation of retinoic acid-resistant neuroblastoma cells
- PMID: 40233178
- PMCID: PMC12145117
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.ads2641
A drug that induces the microRNA miR-124 enables differentiation of retinoic acid-resistant neuroblastoma cells
Abstract
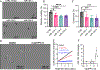
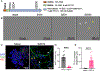
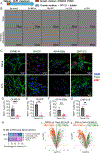
Tumor cell heterogeneity in neuroblastoma, a pediatric cancer arising from neural crest-derived progenitor cells, presents clinical challenges. Unlike adrenergic (ADRN) neuroblastoma cells, neuroblastoma cells with a mesenchymal (MES) identity are resistant to chemotherapy and retinoid therapy, which contributes to relapses and treatment failures. We explored whether up-regulation of the neurogenic, tumor suppressor microRNA miR-124 could promote the differentiation of retinoic acid-resistant MES neuroblastoma cells. Leveraging our screen for miRNA-modulatory small molecules, we identified and validated the tyrosine and phosphoinositide kinase inhibitor PP121 as a robust inducer of miR-124. Combining PP121 and BDNF-activating bufalin synergistically arrested proliferation and promoted the sustained differentiation of MES/heterogeneous SK-N-AS cells over several weeks. This protocol also resulted in the differentiation of multiple MES neuroblastoma and glioblastoma cell lines. RNA-seq analysis of differentiated MES/heterogeneous SK-N-AS cells revealed the replacement of the ADRN core regulatory circuitry with circuitries associated with chromaffin cells and Schwann cell precursors. Furthermore, differentiation was associated with inhibition of the CDK4/CDK6 pathway and activation of a transcriptional program that correlated with improved outcomes for patients with neuroblastoma. Our findings suggest an approach with translational potential to induce the differentiation of therapy-resistant cancers of the nervous system. Moreover, these long-lived, differentiated cells could be used to study mechanisms underlying cancer biology and therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Update of
-
Novel miRNA-inducing drugs enable differentiation of retinoic acid-resistant neuroblastoma cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 29:2024.06.05.597584. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.05.597584. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Sci Signal. 2025 Apr 15;18(882):eads2641. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.ads2641. PMID: 38895399 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Whittle SB et al. , Overview and recent advances in the treatment of neuroblastoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 17, 369–386 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Ross RA, Spengler BA, Biedler JL, Coordinate morphological and biochemical interconversion of human neuroblastoma cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 71, 741–747 (1983). - PubMed
-
- Rettig WJ, Spengler BA, Chesa PG, Old LJ, Biedler JL, Coordinate changes in neuronal phenotype and surface antigen expression in human neuroblastoma cell variants. Cancer Res 47, 1383–1389 (1987). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

