Tailoring an intravenously injectable oncolytic virus for augmenting radiotherapy
- PMID: 40233744
- PMCID: PMC12147856
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102078
Tailoring an intravenously injectable oncolytic virus for augmenting radiotherapy
Abstract
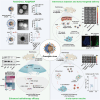
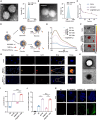
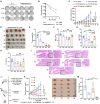
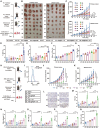
Oncolytic viruses (OVs) combined with radiotherapy (RT) show promise but are limited by challenges such as poor intravenous delivery and insufficient RT-induced DNA damage. In this study, an oncolytic adenovirus (AD) formulation, RadioOnco (AD@PSSP), is developed to improve delivery, infectivity, immune response, and RT efficacy. The multifunctional polyethylenimine (PEI)-selenium-polyethylene glycol (PEG) (PSSP) enhances intravenous delivery, shields the virus from rapid clearance, and enables targeted delivery to tumor sites after RT. The exposed PEI enhances the infectivity of AD through electrostatic interactions, thereby increasing DNA damage after RT by inhibiting the expression of DNA repair proteins, such as CHEK1 and CDK1. Furthermore, AD-PEI captures and delivers RT-induced tumor-released antigens to lymph nodes, activating robust anti-tumor immune responses. Animal model data demonstrate that RadioOnco overcomes RT resistance, targets distant metastases, and promotes long-term immunity, addressing metastasis and recurrence. In summary, this intravenously injectable OV enhances RT synergy through surface modification with multifunctional materials.
Keywords: DNA damage and repair; ROS-responsive materials; adenovirus; anti-tumor immune responses; antigen capture; oncolytic viruses; radiotherapy; radiotherapy resistance; radiotherapy sensitizer; synergistic therapy.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Therapeutic targeting of chitosan-PEG-folate-complexed oncolytic adenovirus for active and systemic cancer gene therapy.J Control Release. 2013 Aug 10;169(3):257-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.03.030. Epub 2013 Apr 4. J Control Release. 2013. PMID: 23562633
-
Potent antitumor effect of neurotensin receptor-targeted oncolytic adenovirus co-expressing decorin and Wnt antagonist in an orthotopic pancreatic tumor model.J Control Release. 2015 Dec 28;220(Pt B):766-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.10.015. Epub 2015 Oct 22. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 26471393
-
Chemical modification with high molecular weight polyethylene glycol reduces transduction of hepatocytes and increases efficacy of intravenously delivered oncolytic adenovirus.Hum Gene Ther. 2009 Sep;20(9):975-88. doi: 10.1089/hum.2009.028. Hum Gene Ther. 2009. PMID: 19469693 Free PMC article.
-
Virus combinations and chemotherapy for the treatment of human cancers.Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2008 Aug;10(4):371-9. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18683102 Review.
-
Progress in oncolytic viruses modified with nanomaterials for intravenous application.Cancer Biol Med. 2023 Nov 24;20(11):830-55. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2023.0275. Cancer Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 38009779 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synergy of oncolytic adenovirus and immune checkpoint inhibitors: transforming cancer immunotherapy paradigms.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 8;16:1610858. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1610858. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40698086 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

