In early rheumatoid arthritis, comorbidities do not explain the increased risk of failure to reach remission in patients with obesity
- PMID: 40234098
- PMCID: PMC12001363
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2025-005430
In early rheumatoid arthritis, comorbidities do not explain the increased risk of failure to reach remission in patients with obesity
Abstract
Objective: To examine whether obesity and/or overweight are independently associated with an increased risk of remission failure in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA), treated with methotrexate as first disease-modifying antirheumatic drug, or if the previously reported associations could be explained by underlying comorbidities and lifestyle factors.
Methods: For patients included in the Epidemiological Investigation of Rheumatoid Arthritis (EIRA) study 2006-2018 initiating methotrexate monotherapy (n=1285), we captured data on body mass index, comorbidities and disease activity from EIRA and through linkage to nationwide Swedish clinical and quality registers. The primary outcome was failure to reach 28-joint Disease Activity Score (DAS28) remission at 3 and 6 months. Secondary outcomes included Boolean, Simplified Disease Activity Index and Clinical Disease Activity Index remission and their individual components. We estimated the relative risk (RR) of remission failure in patients with obesity and overweight compared with normal weight using modified Poisson regression, adjusting for potential confounders.
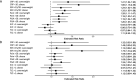
Results: After 6 months, 64% (n=98/153) of patients with obesity, 52% (n=171/326) with overweight and 48% (n=210/433) with normal weight failed to reach DAS28 remission, with an RR of 1.33 (95% CI 1.14 to 1.55) for patients with obesity after adjustment for age and sex. The increased risk of remission failure in patients with obesity remained after further adjustment for seropositivity, educational level, smoking, alcohol use, physical activity, calendar period, glucocorticoid treatment and comorbidities (RR=1.27, 95% CI 1.08 to 1.50). No significant association was observed for patients with overweight. The results were similar for the secondary outcomes and after 3 months.
Conclusion: Obesity is a risk factor for remission failure in early RA, independent of comorbid conditions.
Keywords: Arthritis, Rheumatoid; Epidemiology; Methotrexate; Sweden.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JA has received grants from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BMS, Eli Lily, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi and UCB; these entities have entered into agreements with Karolinska Institutet with JA as principal investigator mainly in the context of safety monitoring of biologics via ARTIS/Swedish Biologics Register. BD has received grants from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BMS, Eli Lilly, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi, UCB, paid to Karolinska Institutet, in the context of the ARTIS national safety monitoring system, used for paying a part of BD’s salary. SS is a part-time employee of deCODE genetics, unrelated to this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comorbidities and chance of remission in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate as first-line therapy: a Swedish observational nationwide study.RMD Open. 2023 Dec 20;9(4):e003714. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003714. RMD Open. 2023. PMID: 38123483 Free PMC article.
-
Overweight decreases the chance of achieving good response and low disease activity in early rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2014 Nov;73(11):2029-33. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-205094. Epub 2014 May 12. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014. PMID: 24818635
-
Overweight, Obesity, and the Likelihood of Achieving Sustained Remission in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results From a Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018 Aug;70(8):1185-1191. doi: 10.1002/acr.23457. Epub 2018 Jul 13. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018. PMID: 29193840
-
Efficacy of initial methotrexate monotherapy versus combination therapy with a biological agent in early rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of clinical and radiographic remission.Ann Rheum Dis. 2010 Jul;69(7):1298-304. doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.118307. Epub 2010 Apr 26. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010. PMID: 20421343 Review.
-
Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: 2014 update of the recommendations of an international task force.Ann Rheum Dis. 2016 Jan;75(1):3-15. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207524. Epub 2015 May 12. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016. PMID: 25969430 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
