Outcomes of patients with relapsed/refractory lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/waldenström macroglobulinemia treated with venetoclax: a multicenter retrospective analysis
- PMID: 40234394
- PMCID: PMC12000436
- DOI: 10.1038/s41408-025-01271-3
Outcomes of patients with relapsed/refractory lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/waldenström macroglobulinemia treated with venetoclax: a multicenter retrospective analysis
Abstract
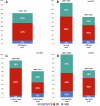
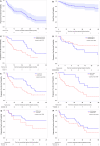
Venetoclax showed promising activity in a small phase II trial in relapsed/refractory Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM). To report the clinical activity of venetoclax and prognostic factors associated with outcomes in a larger cohort, we retrospectively identified 76 patients with relapsed/refractory lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma (LPL)/WM treated with venetoclax monotherapy at nine US medical centers. The median age at venetoclax treatment initiation was 66 years. MYD88, CXCR4, and TP53 mutations were detected in 65 (94%), 23 (40%), and 10 (22%) patients, respectively. The median number of prior lines of treatment was 3, including covalent BTK inhibitor in 82% and alkylating agent in 71% of patients. The overall and major response rates to venetoclax were 70% and 63%, respectively. The median and 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) were 28.5 months and 57%, respectively. The median and 2-year overall survival were not reached and 82%, respectively. Prior treatment with BTK inhibitor was the only factor associated with PFS in multivariate analysis (hazard ratio 2.97, p = 0.012). Venetoclax dose interruptions and/or reductions occurred in 27 patients (41%). Five patients (7%) developed laboratory tumor lysis syndrome (TLS), including 3 (4%) with clinical TLS. Venetoclax resulted in a high response rate and a prolonged PFS in patients with heavily pretreated LPL/WM.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: A.G.C. reports honoraria from Janssen, Sanofi, Cellectar, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Pfizer. A.W. has consulted for BeiGene, BTG Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, and ADC Therapeutics. G.P. is a shareholder of Crispr Therapeutics and equity holder of Mevox Ltd and reports consultancy with ADC Therapeutics. J.J.C. received research funding from Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Beigene, Cellectar, Loxo, and Pharmacyclics, and consulting fees from Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Beigene, Cellectar, Janssen, Loxo, Mustang Bio, Nurix, and Pharmacyclics. K.H.S. reports honoraria from Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Adaptive, Sanofi, Regeneron, and Takeda, and research funding to the institution from AbbVie and Karyopharm, outside the submitted work. PAR reports serving as a consultant and/or advisory board member for AbbVie, Novartis, BMS, ADC Therapeutics, Kite/Gilead, Pfizer, CVS Caremark, Genmab, BeiGene, Janssen, Pharmacyclics, and Genentech/Roche. Honoraria from Adaptive Biotechnologies. Research support from BMS, Kite Pharma, Novartis, CRISPR Therapeutics, Calibr, Xencor, Fate Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, Cellectis, Cargo Therapeutics, and Tessa Therapeutics. P.K. is the principal investigator of trials for which Mayo Clinic has received research funding from Amgen, Regeneron, Bristol Myers Squibb, Loxo Pharmaceuticals, Ichnos, Karyopharm, Sanofi, AbbVie and GlaxoSmithKline. Prashant Kapoor has received honorarium from Keosys and served on the Advisory Boards of BeiGene, Mustang Bio, Janssen, Pharmacyclics, X4 Pharmaceuticals, Kite Pharma, Oncopeptides, Ascentage, Angitia Bio, GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi and AbbVie. SS received research funds or honoraria from Beigene, Cellectar, and ADC Therapeutics. ST received research funding from Ascentage Pharma, BMS, Genentech, Cellectar Biosciences, and Abbvie and has consulted for Cellectar Biosciences. YS received research funding from BeiGene, Genmab, and AbbVie and has consulted for ADC, Genmab, and Genentech.
Figures
References
-
- Castillo JJ, Advani RH, Branagan AR, Buske C, Dimopoulos MA, D'Sa S, et al. Review consensus treatment recommendations from the tenth international workshop for Waldenström Macroglobulinaemia. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7:e827–37. 10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30224-6 - PubMed
-
- Cao Y, Yang G, Hunter ZR, Liu X, Xu L, Chen J, et al. The BCL2 antagonist ABT-199 triggers apoptosis, and augments ibrutinib and idelalisib mediated cytotoxicity in CXCR4Wild-type and CXCR4WHIM mutated Waldenstrom macroglobulinaemia cells. Br J Haematol. 2015;170:134–8. 10.1111/bjh.13278 - PubMed
-
- Kumar SK, Callander NS, Adekola K, Anderson LD Jr, Baljevic M, Baz R, et al. Waldenström Macroglobulinemia/Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma, Version 2.2024, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2024;22:e240001. 10.6004/jnccn.2024.0001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

