Memantine abrogates testicular dysfunction induced by risperidone in rats with a potential role of ERK1/2-Nrf2-caspase-3 signaling pathway
- PMID: 40234489
- PMCID: PMC12000432
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-94760-1
Memantine abrogates testicular dysfunction induced by risperidone in rats with a potential role of ERK1/2-Nrf2-caspase-3 signaling pathway
Abstract
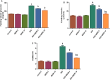
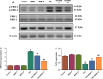
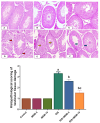
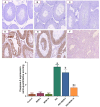
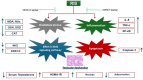
Psychosis is usually a substantial global burden with a prevalence of 0.4-2%. On the other hand, 50 million people are suffering from dementia, with dementia-related psychosis affecting approximately 25% of them. The current experiment aimed to investigate the effect of the anti-dementia drug memantine (MEM) on testicular damage and insulin resistance induced by the chronic administration of risperidone (RIS) in rats. Six groups of Wistar albino rats were designated as follows: control, MEM-5 (rats received MEM at 5 mg/kg/day, orally, for 4 weeks), MEM-10 (rats received MEM at 10 mg/kg/day, orally, for 4 weeks), RIS (rats were administered RIS at 2.5 mg/kg/day, orally, for 4 weeks), RIS + MEM-5 (rats received MEM at 5 mg/kg/day, orally, co-administered with RIS as in the RIS group for 4 weeks), and RIS + MEM-10 (rats received MEM at 10 mg/kg/day, orally, co-administered with RIS as in the RIS group for 4 weeks). The duration of the study was 28 days. Serum testosterone, resistin, and adiponectin concentrations were determined. The homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) was also evaluated. Oxidative stress, inflammatory markers, and immunoblotting of ERK1/2, and Nrf2 were quantified in testicular tissue together with histopathological evaluation and a caspase-3 immunohistochemical study. MEM co-administration increased adiponectin, serum testosterone, GSH, SOD, CAT, and Nrf2 expression while decreasing HOMA-IR, resistin, MDA, NOx, ERK1/2, IL-6, TNF-α, NFĸB, and caspase-3 expression. Furthermore, MEM ameliorated all measured parameters and histopathological changes that occurred in the RIS group in a dose-dependent manner. The primary outcomes were attained by attenuating oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in the testis caused by chronic RIS administration via regulation of the ERK1/2-Nrf2 signaling pathway. Targeting the ERK1/2-Nrf2 pathway is a potential strategy for addressing testicular injury.
Keywords: Anti-dementia; Antipsychotics; Memantine; Reproductive toxicity; Risperidone.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: The study was approved by the institutional ethical committee (Faculty of Medicine, Minia University Egypt, Approval No.28:3/2021).
Figures
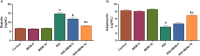
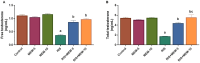
References
-
- Tendilla-Beltrán, H. et al. Neuroplasticity and inflammatory alterations in the nucleus accumbens are corrected after risperidone treatment in a schizophrenia-related developmental model in rats. Schizophr. Res.235 17–28 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

