Genetic associations of plasma proteins and breast cancer identify potential therapeutic drug candidates
- PMID: 40234727
- PMCID: PMC12000288
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-08046-3
Genetic associations of plasma proteins and breast cancer identify potential therapeutic drug candidates
Abstract
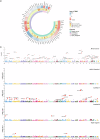
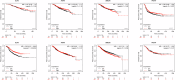
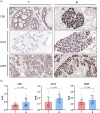
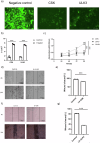
To address the pressing need to improve breast cancer outcomes, we identify 9 plasma proteins with significant associations to breast cancer, namely ULK3, CSK, ASIP, TLR1 in breast cancer, ADH5, SARS2, ULK3, UBE2N in Luminal A subtype, PEX14 in Luminal B subtype. Tumor immune cell infiltration analysis and mutation phenotypes in mice further demonstrate a complex pattern of interaction between these genes and immune responses. Compared to normal tissues, tumor tissues exhibit reduced expression of ULK3 and CSK. Notably, elevated ULK3 expression in both breast cancer and the Luminal A subtype is significantly associated with prolonged recurrence-free survival. Overexpression of CSK and ULK3 is confirmed to significantly inhibit the proliferation and migratory ability of MCF-7 cells. Additionally, three drug candidates-TG100801, Hydrochlorothiazide, and Imatinib-show promise in targeting these proteins, contributing valuable insights for prioritizing drug development in realm of breast cancer.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Tan, J. S., Liu, N. N., Guo, T. T., Hu, S. & Hua, L. Genetic predisposition to COVID-19 may increase the risk of hypertension disorders in pregnancy: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Pregnancy Hypertension26, 17–23 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

