Follow-up of long COVID based on the definition of WHO: a multi-centre cross-sectional questionnaire-based study
- PMID: 40234823
- PMCID: PMC11998132
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-025-22671-x
Follow-up of long COVID based on the definition of WHO: a multi-centre cross-sectional questionnaire-based study
Abstract
Background: Since long COVID has hindered people from normal life, it is essential to understand its full spectrum of manifestation. However, it was heterogeneous in the existing studies and few large-scale studies have been conducted on Asian populations. Here, we conducted a multi-centre questionnaire-based study among Chinese people to explore the long COVID based on the definition of WHO.
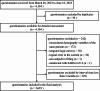
Methods: During March 20, 2023 and June 18, 2023, individuals with a history of confirmed or self-reported SARS-CoV-2 infection were recruited from three hospitals to fill out the questionnaire for long COVID. Each symptom was assigned with 0 to 3 points based on their severity. And the long COVID score was a sum of these points of each symptom. The reporting rate, time trend and risk factors of long COVID stratified by different systems were explored.
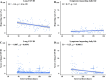
Results: 3,693 individuals were recruited for the study. The reporting rate of at least one persistent long COVID symptoms and symptoms impacting daily life was 30.2% (1,117) and 10.7% (394). Systemic symptoms (20.7%, 765) were most easily reported. The most common symptoms were fatigue (16.3%, 602), cough (6.3%, 234) and expectoration (5.5%, 203). The reporting rate of long COVID and long COVID score decreased over time during a 180-day follow-up period (P < 0.05). For long COVID, older age (OR: 1.63, 1.38-1.93), female (OR: 1.19, 1.03-1.38) and SARS-CoV-2 reinfection (OR: 3.56, 2.63-4.80) were risk factors; while number of COVID-19 vaccine doses (OR: 0.87, 0.81-0.94) was a protective factor. The use of traditional Chinese medicine (OR: 0.51, 0.37-0.71) was a protective factor for symptoms impacting daily life.
Conclusions: Early interventions should be taken to minimize the impact of long COVID, especially for the elderly, females and those with SARS-CoV-2 reinfection. COVID-19 booster vaccination might play a potential role in minimizing the impact of long COVID.
Keywords: COVID-19; Long COVID; Post COVID-19 syndrome; Survey.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The Ethical approval was granted by the First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University ethical committee (2023004A01). Informed consent was obtained from all subjects and/or their legal guardian(s). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Skevaki C, Moschopoulos CD, Fragkou PC, et al. Long COVID: pathophysiology, current concepts, and future directions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024. 10.1016/j.jaci.2024.12.1074. - PubMed
-
- Crook H, Raza S, Nowell J, Young M, Edison P. Long covid-mechanisms, risk factors, and management. BMJ. 2021. 10.1136/bmj.n1648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- XGZ2301/Academy Level Project of the First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University
- Evaluation of the effect of traditional Chinese medicine on the elderly patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019/Zhejiang Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Project
- LTGG23H260002/Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- Y23H190011/Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023QL055/Youth Science and Technology Innovation Leading Talent project of Ningbo
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

