PFLO: a high-throughput pose estimation model for field maize based on YOLO architecture
- PMID: 40234900
- PMCID: PMC11998432
- DOI: 10.1186/s13007-025-01369-6
PFLO: a high-throughput pose estimation model for field maize based on YOLO architecture
Abstract
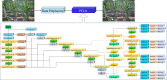
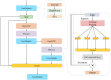
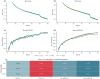
Posture is a critical phenotypic trait that reflects crop growth and serves as an essential indicator for both agricultural production and scientific research. Accurate pose estimation enables real-time tracking of crop growth processes, but in field environments, challenges such as variable backgrounds, dense planting, occlusions, and morphological changes hinder precise posture analysis. To address these challenges, we propose PFLO (Pose Estimation Model of Field Maize Based on YOLO Architecture), an end-to-end model for maize pose estimation, coupled with a novel data processing method to generate bounding boxes and pose skeleton data from a"keypoint-line"annotated phenotypic database which could mitigate the effects of uneven manual annotations and biases. PFLO also incorporates advanced architectural enhancements to optimize feature extraction and selection, enabling robust performance in complex conditions such as dense arrangements and severe occlusions. On a fivefold validation set of 1,862 images, PFLO achieved 72.2% pose estimation mean average precision (mAP50) and 91.6% object detection mean average precision (mAP50), outperforming current state-of-the-art models. The model demonstrates improved detection of occluded, edge, and small targets, accurately reconstructing skeletal poses of maize crops. PFLO provides a powerful tool for real-time phenotypic analysis, advancing automated crop monitoring in precision agriculture.
Keywords: Computer vision; Deep learning; In-field monitoring; Maize; Plant pose estimation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures













References
-
- Runge CF, Senauer B. How biofuels could starve the poor. Foreign Aff. 2007;86:41.
-
- Shiferaw B, Prasanna BM, Hellin J, Bänziger M. Crops that feed the world 6. Past successes and future challenges to the role played by maize in global food security. Food Secur. 2011;3:307–27.
-
- Moulia B, Coutand C, Lenne C. Posture control and skeletal mechanical acclimation in terrestrial plants: implications for mechanical modeling of plant architecture. Am J Bot. 2006;93(10):1477–89. - PubMed
-
- Furbank RT, Tester M. Phenomics–technologies to relieve the phenotyping bottleneck. Trends Plant Sci. 2011;16(12):635–44. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

