The GluN3-containing NMDA receptors
- PMID: 40235311
- PMCID: PMC12005412
- DOI: 10.1080/19336950.2025.2490308
The GluN3-containing NMDA receptors
Abstract
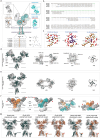
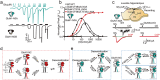
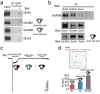
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) are heterotetrameric ion channels that play crucial roles in brain function. Among all the NMDAR subtypes, GluN1-N3 receptors exhibit unique agonist binding and gating properties. Unlike "conventional" GluN1-N2 receptors, which require both glycine and glutamate for activation, GluN1-N3 receptors are activated solely by glycine. Furthermore, GluN1-N3 receptors display faster desensitization, reduced Ca2+ permeability, and lower sensitivity to Mg2+ blockage compared to GluN1-N2 receptors. Due to these characteristics, GluN1-N3 receptors are thought to play critical roles in eliminating redundant synapses and pruning spines in early stages of brain development. Recent studies have advanced pharmacological tools for specifically targeting GluN1-N3 receptors and provided direct evidence of these glycine-activated excitatory receptors in native brain tissue. The structural basis of GluN1-N3 receptors has also been elucidated through cryo-EM and artificial intelligence. These findings highlight that GluN1-N3 receptors are not only involved in essential brain functions but also present potential targets for drug development.
Keywords: Ionotropic glutamate receptors; ligand-gated ion channels; pathology and physiology; protein prediction; synaptic transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structure-based discovery of antagonists for GluN3-containing N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors.Neuropharmacology. 2013 Dec;75:324-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.08.003. Epub 2013 Aug 22. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23973313 Free PMC article.
-
Negative allosteric modulation of GluN1/GluN3 NMDA receptors.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Oct 1;176:108117. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108117. Epub 2020 May 7. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32389749 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into assembly and function of GluN1-2C, GluN1-2A-2C, and GluN1-2D NMDARs.Mol Cell. 2022 Dec 1;82(23):4548-4563.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.10.008. Epub 2022 Oct 28. Mol Cell. 2022. PMID: 36309015 Free PMC article.
-
Glycine agonism in ionotropic glutamate receptors.Neuropharmacology. 2021 Aug 1;193:108631. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108631. Epub 2021 May 28. Neuropharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34058193 Review.
-
The roles of GluN3-containing N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor in central nerve system.Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021 Oct 25;50(5):651-658. doi: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2021-0167. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021. PMID: 34986531 Free PMC article. Review. English.
Cited by
-
Artificial intelligence insight on structural basis and small molecule binding niches of NMDA receptor.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025 Jul 14;27:3167-3180. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2025.07.027. eCollection 2025. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 40727426 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of NMDA receptors: 2015-2024.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 6;16:1614831. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1614831. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40548058 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the evolution of kainate receptor research over five decades: trends, hotspots, and emerging frontiers.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Aug 23. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04540-x. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40848135
-
Inactivation of NMDAR and CaMKII signaling within the prelimbic cortex blocks incubated cocaine- and sucrose-craving.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 15:2025.07.10.664193. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.10.664193. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40791399 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
