Normalization and cross-entropy connectivity in brain disease classification
- PMID: 40235587
- PMCID: PMC11999650
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112226
Normalization and cross-entropy connectivity in brain disease classification
Abstract
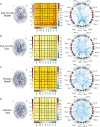
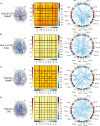
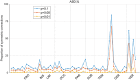
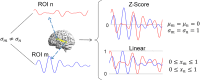
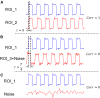
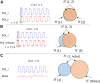
In resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI), Pearson correlation has traditionally been the dominant method for constructing brain connectivity. This paper introduces an entropy-based connectivity approach utilizing subject-level Z score normalization, which not only standardizes signal amplitudes across subjects but also preserves interregional signal differences more effectively than Pearson correlation. Furthermore, the proposed method incorporates cross-entropy techniques, offering an advanced perspective on the temporal ordering of signals between brain regions rather than merely capturing their synchronization. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed subject-normalized cross-joint entropy achieves superior classification accuracy in schizophrenia, mild cognitive impairment, and autism spectrum disorder, outperforming the conventional normalized correlation method by approximately 4%, 6%, and 7%, respectively. Additionally, the observed performance improvement may be attributed to changes in the symmetry of functional connectivity between brain regions-an aspect often overlooked in traditional functional connectivity analyses.
Keywords: Biocomputational method; Mathematical biosciences; Neuroscience.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

