Spectral computed tomography parameters for predicting vessels encapsulating tumor clusters (VETC) pattern in hepatocellular carcinoma: a pilot study
- PMID: 40235763
- PMCID: PMC11994570
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-24-2077
Spectral computed tomography parameters for predicting vessels encapsulating tumor clusters (VETC) pattern in hepatocellular carcinoma: a pilot study
Abstract
Background: Vessels encapsulating tumor clusters (VETC) is a novel microvascular pattern associated with poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Reliable preoperative predictors of VETC may substantially improve prognostic outcomes. This study aimed to evaluate the predictive value of multiparameter spectral computed tomography (CT) in identifying VETC pattern in HCC.
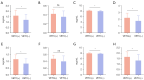
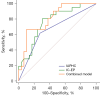
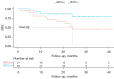
Methods: This retrospective analysis included 50 patients with histopathologically confirmed HCC who underwent preoperative abdominal spectral CT and CD34 immunohistochemical staining. VETC(+) was defined as a visible vessel-encapsulating tumor cluster occupying ≥5% of the tumor area. Patients were divided into VETC(+) (n=21) and VETC(-) (n=29) groups. Eight qualitative imaging features, including tumor size, intratumor vascularity, nonrim arterial phase (AP) hyperenhancement, nonperipheral portal phase (PP) washout, well-defined capsule, nonsmooth tumor margin, intratumoral necrosis, and AP hypovascular component, were assessed via 40-keV virtual monoenergetic images (VMIs). Quantitative spectral parameters, including iodine concentration (IC), normalized IC (NIC), effective atomic number (Zeff), and energy spectrum curve slope (λ), were measured in both the PP and equilibrium phase (EP). Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to identify independent risk factors for VETC pattern, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was used to evaluate the diagnostic performance, and the Kaplan-Meier method was used to assess recurrence-free survival (RFS).
Results: Significant differences were found between the VETC(+) and VETC(-) groups in alpha-fetoprotein level, intratumor AP hypovascular component (IAPHC), and portal- and equilibrium-phase spectral parameters (IC, Zeff, and λ; all P values <0.05). Multivariate logistic regression identified the IAPHC and EP IC as independent VETC predictors of VETC patter [odds ratio (OR) =4.149 and OR =12.724, respectively]. The combined model demonstrated superior diagnostic performance (AUC =0.810) compared to the individual parameters (IAPHC: AUC =0.672; EP IC: AUC =0.766), achieving a 66.67% sensitivity and an 89.66% specificity. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis indicated a shorter RFS in the VETC(+) group than in the VETC(-) group (P=0.02).
Conclusions: IAPHC and EP IC derived from spectral CT hold significant potential for VETC prediction in HCC. The application of a combined model enhances diagnostic efficiency.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); differential diagnosis; spectral computed tomography (spectral CT); vessels encapsulating tumor clusters (VETC).
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://qims.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/qims-24-2077/coif). X.C. is an employee of Philips Healthcare, the manufacturer of the CT system used in this study. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Fang JH, Zhou HC, Zhang C, Shang LR, Zhang L, Xu J, Zheng L, Yuan Y, Guo RP, Jia WH, Yun JP, Chen MS, Zhang Y, Zhuang SM. A novel vascular pattern promotes metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma in an epithelial-mesenchymal transition-independent manner. Hepatology 2015;62:452-65. 10.1002/hep.27760 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li Z, Song W, Zhang J, Li Q, Song Z, Ren X, Wen Y, Li X, Yao H, Gao Y, Tang Z. Identification of vessels encapsulating tumor clusters in solitary hepatocellular carcinoma via imaging biomarkers in preoperative contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Quant Imaging Med Surg 2024;14:8586-600. 10.21037/qims-24-315 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
