Design and screening of novel endosomal escape compounds that enhance functional delivery of oligonucleotides in vitro
- PMID: 40235852
- PMCID: PMC11999280
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102522
Design and screening of novel endosomal escape compounds that enhance functional delivery of oligonucleotides in vitro
Abstract
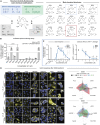
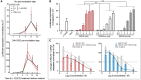
Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), including splice-switching oligonucleotides (SSOs), are promising therapeutic approaches for targeting genetic defects. ASOs act in the nucleus and the cytosol to cleave mRNAs via the RNaseH1 mechanism (e.g., gapmers), while SSOs alter transcript splicing to restore or inhibit protein function. RNA interference (RNAi) is another approach to down-regulate gene expression via the RISC complex. However, a major challenge is the effective delivery of these nucleic acid-based therapeutics. Recent developments focus on enhancing cellular uptake and endosomal release, including the use of small-molecule endosomal escape enhancers (EEEs) such as chloroquine. Here, we disclose a next generation of EEEs, which efficiently enhance SSOs and gapmers in vitro activity. We identify proton sponge-mediated endosomal leakage as a mechanism of action and observe, by Gene Ontology analysis on bulk RNA sequencing, that EEE treatment increased gene expression of markers associated with vesicle organization. Additionally, using primary human hepatocytes, we demonstrate that EEEs enhance small interfering RNA (siRNA) activity. Unconjugated siRNA reached similar levels of mRNA knockdown to the observed GalNAc-conjugated siRNA. Substantial GalNAc conjugated siRNA enhancement was also observed when used together with EEE. Our results indicate that these EEEs constitute a promising strategy to enhance the activity of multimodal oligonucleotide therapeutics.
Keywords: MT: Oligonucleotides: Therapies and Applications; antisense; endosomes; enhancers; leakage; lysosomes; mitophagy; oligonucleotides; small molecules; therapeutic.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
H.Y.E., O.G., S.A., J.B., S.E.L.A., and A.D. are listed as inventors on an international patent application entitled “Compositions and Methods for Delivering a Macromolecule to a Cell.” T.B., M.J.M., D.K.B., D. Hekman, S.A., and A.D. are employees of AstraZeneca.
Figures




References
-
- Bennett C.F., Swayze E.E. RNA targeting therapeutics: Molecular mechanisms of antisense oligonucleotides as a therapeutic platform. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010;50:259–293. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

