This is a preprint.
Epidermal Resident Memory T Cell Fitness Requires Antigen Encounter in the Skin
- PMID: 40236062
- PMCID: PMC11996394
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.03.31.646438
Epidermal Resident Memory T Cell Fitness Requires Antigen Encounter in the Skin
Abstract
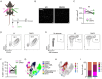
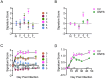
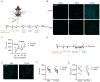
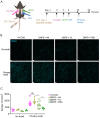
CD8+ tissue resident memory T cells (TRM) develop from effectors that seed peripheral tissues where they persist providing defense against subsequent challenges. TRM persistence requires autocrine TGFβ transactivated by integrins expressed on keratinocytes. TRM precursors that encounter antigen in the epidermis during development outcompete bystander TRM for TGFβ resulting in enhanced persistence. ScRNA-seq analysis of epidermal TRM revealed that local antigen experience in the skin resulted in an enhanced differentiation signature in comparison with bystanders. Upon recall, TRM displayed greater proliferation dictated by affinity of antigen experienced during epidermal development. Finally, local antigen experienced TRM differentially expressed TGFβRIII, which increases avidity of the TGFβRI/II receptor complex for TGFβ. Selective ablation of Tgfbr3 reduced local antigen experienced TRM capacity to persist, rendering them phenotypically like bystander TRM. Thus, antigen driven TCR signaling in the epidermis during TRM differentiation results in a lower TGFβ requirement for persistence and increased proliferative capacity that together enhance epidermal TRM fitness.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: D.H.K is a paid consultant for AbbVie Inc, Beiersdorf AG, Janssen Research and Development LLC, and Aditum Bio. DHK has a sponsored research agreement with Galderma Laboratories, Lp. N.A. serves as a consultant or is on the advisory board for : Shennon Biotechnologies, Panther Life Sciences, Verrica pharmaceuticals, Genmab, 23 and me, Johnson and Johnson, Lytix Biopharma. Other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Virassamy B., et al. , Intratumoral CD8(+) T cells with a tissue-resident memory phenotype mediate local immunity and immune checkpoint responses in breast cancer. Cancer Cell, 2023. 41(3): p. 585–601.e8. - PubMed
-
- Strobl J., et al. , Long-term skin-resident memory T cells proliferate in situ and are involved in human graft-versus-host disease. Sci Transl Med, 2020. 12(570).
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
