This is a preprint.
Acquired Amphotericin B Resistance Attributed to a Mutated ERG3 in Candidozyma auris
- PMID: 40236146
- PMCID: PMC11996407
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.03.30.646105
Acquired Amphotericin B Resistance Attributed to a Mutated ERG3 in Candidozyma auris
Update in
-
Acquired amphotericin B resistance attributed to a mutated ERG3 in Candidozyma auris.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025 Nov 5;69(11):e0060125. doi: 10.1128/aac.00601-25. Epub 2025 Sep 22. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025. PMID: 40980913 Free PMC article.
Abstract
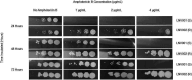
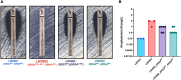
First identified in 2009, Candidozyma auris (formerly Candida auris) is an emerging multidrug resistant fungus that can cause invasive infections with a crude mortality rate ranging from 30-60%. Currently, 30-50% of C. auris isolates are intrinsically resistant to amphotericin B. In this work, we characterized a clinical case of acquired amphotericin B resistance using whole genome sequencing, a large-scale phenotypic screen, comprehensive sterol profiling, and genotypic reversion using CRISPR. Data obtained in this work provides evidence that a deletion resulting in a frameshift in ERG3 contributes to the observed resistant phenotype. Characterization of this isolate also revealed a fitness cost is associated with the abrogation of ergosterol production and its replacement with other late-stage sterols. This article presents a clinical case description of amphotericin B resistance from a frameshift mutation in ERG3 in C. auris and marks an advancement in the understanding of antifungal resistance in this fungal pathogen.
Figures

References
-
- @CDCgov. 2019 Antibiotic Resistance Threats Report | CDC. 2022. 2022-07-15T02:03:14Z [cited; Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/biggest-threats.html.
-
- Liu F, Hu Z-D, Zhao X-M, Zhao W-N, Feng Z-X, Yurkov A, et al. Phylogenomic analysis of the Candida auris- Candida haemuli clade and related taxa in the Metschnikowiaceae, and proposal of thirteen new genera, fifty-five new combinations and nine new species. Persoonia - Molecular Phylogeny and Evolution of Fungi. 2024. 2024-06-30;52(1):22–43. - PMC - PubMed
-
- @CDCgov. Increasing Threat of Spread of Antimicrobial-resistant Fungus in Healthcare Facilities | CDC Online Newsroom | CDC. 2023. 2023-03-20T09:01:41Z.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
