Effects of sevoflurane and isoflurane on acute myocardial infarction model establishment in mice
- PMID: 40236295
- PMCID: PMC11999574
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102000
Effects of sevoflurane and isoflurane on acute myocardial infarction model establishment in mice
Abstract
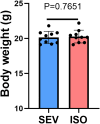
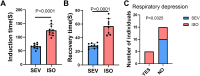
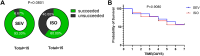
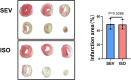
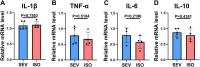
The selection of anesthetic drugs in the preparation of an acute myocardial infarction (AMI) model is very important. We specifically focus on various effects of sevoflurane and isoflurane in a murine AMI model, which have not been previously compared. Furthermore, we evaluated success of our AMI model using following methods: echocardiography, TTC staining, and PCR testing. The results show that compared to the isoflurane group, the sevoflurane group mice had shorter anesthetic induction(66.40 ± 2.90S vs. 125.10 ± 6.30S P < 0.0001) and recovery times(28.00 ± 1.07S vs. 56.88 ± 4.14S, P < 0.0001), lower incidence of respiratory depression (0 % vs. 50.00 %, P = 0.0325), and more successful models (93.33 % vs. 60.00 %, P = 0.0801). There were no significant differences in cardiac function, infarction area(49.41 ± 4.18 % vs. 48.66 ± 3.79 %, P = 0.5266), or inflammatory factors in the myocardial infarction area between the two groups. Sevoflurane may therefore be a better choice for the establishment of AMI models in mice.
Keywords: Acute myocardial infarction; Animal model; Inhalation anesthetics; Mice.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

