Moringa oleifera leaves protein suppresses T-lymphoblastic leukemogenesis via MAPK/AKT signaling modulation of apoptotic activation and autophagic flux regulation
- PMID: 40236708
- PMCID: PMC11996636
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1546189
Moringa oleifera leaves protein suppresses T-lymphoblastic leukemogenesis via MAPK/AKT signaling modulation of apoptotic activation and autophagic flux regulation
Abstract
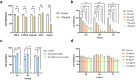
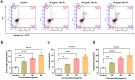
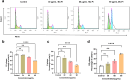
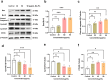
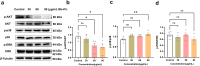
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is one of the most common hematologic malignancies in children worldwide. Despite advances in chemotherapy in recent years, more than 50% of adult T-ALL patients still experience treatment resistance and relapse/refractory disease. Moringa oleifera, a new food resource in China, has high nutritional value and various pharmacological activities. Moringa oleifera protein is one of the main active ingredients in Moringa oleifera leaves, and some studies have shown that Moringa oleifera protein has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, anticancer, and other bioactivities; however, the anti-acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) activity of the Moringa oleifera protein and its mechanism of action are still unclear. In this study, we used Moringa oleifera leaves protein as the experimental material and used the MTT assay, flow cytometry, and Western blot techniques to study the effects of Moringa oleifera leaves protein on Jurkat cell growth, apoptosis, and the cell cycle in vitro and the underlying molecular mechanism. Moringa oleifera leaves protein inhibited Jurkat cell proliferation; induced apoptosis and cycle arrest; increased autophagy; and inhibited Jurkat cell proliferation by regulating the MAPK/AKT pathway. The results of this study provide new ideas and a theoretical basis for the development of Moringa oleifera leaves protein for the prevention and treatment of leukemia.
Keywords: Jurkat cells; MAPK/AKT signaling pathway; Moringa oleifera leaves protein; autophagy; cell proliferation; immunosuppression.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Yang, Xie, Wang, Tian and Song.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Horwath M, Benin V. Theoretical investigation of a reported antibiotic from the “Miracle Tree” Moringa oleifer Lam. Comput Theor Chem. (2011) 965:196–201. doi: 10.1016/j.comptc.2011.01.045 - DOI
-
- Hany MRA-L, Mohamed MA-D, Mustafa S, Joanna N, Dariusz K. Benefits and applications of Moringa oleifera as a plant protein source in Aquafeed: A review. Aquaculture. (2021) 547:737369. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737369 - DOI
-
- Paul CW, Didia BC. The effects of methanolic extract of Moringa oleifera lam roots on the histology of ovary and female reproductive tract of Guinea pigs. Transp Res Rec. (2012) 4:55–60.
-
- Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China . Approval of Moringa oleifera as a new food resource. (2012) 1:.
-
- Zhang X, Chen Z, Li M, Li G, Song Y. Medicinal properties and applications of Moringa oleifera in traditional Chinese medicine. J Ethnopharmacol. (2015) 165:123. doi: 10.1016/ijep.2015.02.024 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

