Pyroptosis for osteoarthritis treatment: insights into cellular and molecular interactions inflammatory
- PMID: 40236711
- PMCID: PMC11996656
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1556990
Pyroptosis for osteoarthritis treatment: insights into cellular and molecular interactions inflammatory
Abstract
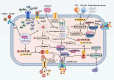
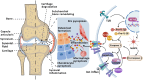
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a widely prevalent chronic degenerative disease often associated with significant pain and disability. It is characterized by the deterioration of cartilage and the extracellular matrix (ECM), synovial inflammation, and subchondral bone remodeling. Recent studies have highlighted pyroptosis-a form of programmed cell death triggered by the inflammasome-as a key factor in sustaining chronic inflammation. Central to this process are the inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interleukin-18 (IL-18), which play crucial roles mediating intra-articular pyroptosis through the NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome. This paper investigates the role of the pyroptosis pathway in perpetuating chronic inflammatory diseases and its linkage with OA. Furthermore, it explores the mechanisms of pyroptosis, mediated by nuclear factor κB (NF-κB), the purinergic receptor P2X ligand-gated ion channel 7 (P2X7R), adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK), and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α). Additionally, it examines the interactions among various cellular components in the context of OA. These insights indicate that targeting the regulation of pyroptosis presents a promising therapeutic approach for the prevention and treatment of OA, offering valuable theoretical perspectives for its effective management.
Keywords: NLRP3; chondrocytes; inflammatory cytokines; osteoarthritis; pyroptosis; synoviocytes.
Copyright © 2025 Lin, Zhang, Li, Li, Gou, He, Lv and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pectolinarigenin targeting FGFR3 alleviates osteoarthritis progression by regulating the NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome pyroptotic pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Oct 25;140:112741. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112741. Epub 2024 Aug 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39094365
-
Activating Nrf2 signalling alleviates osteoarthritis development by inhibiting inflammasome activation.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Nov;24(22):13046-13057. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15905. Epub 2020 Sep 23. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32965793 Free PMC article.
-
P2X7 Receptor Induces Pyroptotic Inflammation and Cartilage Degradation in Osteoarthritis via NF-κB/NLRP3 Crosstalk.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Jan 16;2021:8868361. doi: 10.1155/2021/8868361. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 33532039 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of the Innate Immune Response to Gout.Immunol Invest. 2023 Apr;52(3):364-397. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2023.2168554. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Immunol Invest. 2023. PMID: 36745138 Review.
-
The mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome/pyroptosis activation and their role in diabetic retinopathy.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 25;14:1151185. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1151185. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37180116 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

