HLF and PPARα axis regulates metabolic-associated fatty liver disease through extracellular vesicles derived from the intestinal microbiota
- PMID: 40236774
- PMCID: PMC11995174
- DOI: 10.1002/imt2.70022
HLF and PPARα axis regulates metabolic-associated fatty liver disease through extracellular vesicles derived from the intestinal microbiota
Abstract
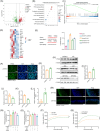
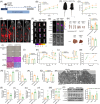
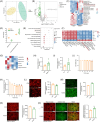
Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) has become increasingly widespread. The intestine is the primary site of lipid absorption and is important for the homeostasis of lipid metabolism. However, the mechanism underlying the participation of the intestinal tract in the development of MAFLD requires additional investigation. In this study, analysis of the single-cell transcriptome of intestinal tissue from cynomolgus monkeys found that hepatic leukemia factor (HLF) participated in the genetic regulation of intestinal lipid absorption. Results obtained from normal and intestine-specific Hlf-knockout mice confirmed that HLF alleviated intestinal barrier disorders by inhibiting peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) expression. The HLF/PPARα axis alleviated MAFLD by mediating gut microbiota-derived extracellular vesicles (fEVs), thereby inhibiting hepatocyte ferroptosis. Lipidomics and functional experiments verified that taurochenodeoxycholic acid (TCDCA), a conjugated bile acid contained in the fEVs, had a key role in the process. In conclusion, intestinal HLF activity was mediated by fEVs and identified as a novel therapeutic target for MAFLD.
Keywords: HLF; MAFLD; bile acids; extracellular vesicles; ferroptosis; gut microbiome.
© 2025 The Author(s). iMeta published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of iMeta Science.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Pipitone, Rosaria Maria , Ciccioli Carlo, Infantino Giuseppe, La Mantia Claudia, Parisi Stefanie, Tulone Adele, Pennisi Grazia, Grimaudo Stefania, and Petta Salvatore. 2023. “MAFLD: A Multisystem Disease.” Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism 14: 20420188221145549. 10.1177/20420188221145549 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
