Dysfunctional glucose metabolism triggers oxidative stress to induce kidney injury in diabetes
- PMID: 40236851
- PMCID: PMC11947919
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.102554
Dysfunctional glucose metabolism triggers oxidative stress to induce kidney injury in diabetes
Abstract
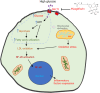
In this editorial, we discussed the article published in the recent issue of the World Journal of Diabetes. To understand the effect of mizagliflozin on kidney injury induced by diabetes, we focused on the mechanisms by which high glucose triggers oxidative stress and contributes to kidney injury in diabetes. The high level of unmetabolized glucose reaching the kidney triggers glucose reabsorption by renal tubules, which elevates the cellular glucose level of renal cells. High glucose induces lactate dehydrogenase overexpression and thus shifts glucose metabolism, which causes mitochondrial dysfunction. Mitochondria generate approximately 90% of the reactive oxygen species in cells, whose dysfunction further alters glucose metabolism and enhances reactive oxygen species generation. Oxidative stress stimulates proinflammatory factor production and kidney inflammatory injury. Mizagliflozin decreases glucose reabsorption and thus ameliorates diabetes-induced kidney injury.
Keywords: Glucose metabolism; Glucose reabsorption; Inflammation; Mitochondrial dysfunction; Reactive oxygen species; Sodium-D-glucose cotransporter 1.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors declare no conflict of interest in publishing the manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Luc K, Schramm-Luc A, Guzik TJ, Mikolajczyk TP. Oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in prediabetes and diabetes. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019;70 - PubMed
-
- Hernandez LF, Eguchi N, Whaley D, Alexander M, Tantisattamo E, Ichii H. Anti-Oxidative Therapy in Diabetic Nephropathy. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 2022;14:14. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

