Best Practices in NMR Metabolomics: Current State
- PMID: 40237011
- PMCID: PMC11999570
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trac.2023.117478
Best Practices in NMR Metabolomics: Current State
Abstract
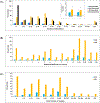
A literature survey was conducted to identify current practices used by NMR metabolomics investigators when conducting and reporting their metabolomics studies. A total of 463 papers from 2020 and 80 papers from 2010 were selected from PubMed and were manually analyzed by a team of investigators to assess the extent and completeness of the experimental procedures and protocols reported. A significant number of the papers did not report on essential experimental details, incompletely stated which statistical methods were used, improperly applied supervised multivariate statistical analyses, or lacked validation of statistical models. A large diversity of protocols and software were identified, which suggests a lack of consensus and a relatively limited use of commonly agreed upon standards for conducting and reporting NMR metabolomics studies. The overall intent of the survey is to inform and encourage the NMR metabolomics community to develop and adopt best-practices for the field.
Keywords: Best Practices; Literature survey; Metabolomics; NMR.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
