Performance of 2 Finger-Stick Blood Tests to Triage Adults With Symptoms of Pulmonary Tuberculosis: A Prospective Multisite Diagnostic Accuracy Study
- PMID: 40237453
- PMCID: PMC12596368
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciaf105
Performance of 2 Finger-Stick Blood Tests to Triage Adults With Symptoms of Pulmonary Tuberculosis: A Prospective Multisite Diagnostic Accuracy Study
Abstract
Background: Non-sputum-based, point-of-care triage tests for pulmonary tuberculosis could enhance tuberculosis diagnostic programs. We assessed the diagnostic accuracy of 2 finger-stick blood tests: the Cepheid 3 gene host-response cartridge (Xpert-HR), which measures 3 host messenger RNA transcripts, and the 3-host protein multibiomarker test (MBT).
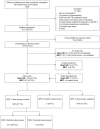
Methods: We performed a prospective diagnostic accuracy study of consecutive participants with symptoms compatible with pulmonary tuberculosis in The Gambia, South Africa, Uganda, and Vietnam. A composite reference standard for active pulmonary tuberculosis incorporated chest radiography, symptom resolution, and sputum microbiological test results. A training-test set approach was used to evaluate test cutoff specificities at 90% sensitivity.
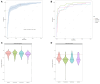
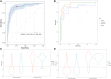
Results: Between 1 November 2020 and 1 May 2023, we screened 1262 participants aged 12-70 years with cough lasting >2 weeks and another symptom suggestive of tuberculosis. Of those who were classifiable by reference tests, 1154 participants had evaluable Xpert-HR results and 961 had evaluable MBT results. Xpert-HR had an area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curve of 0.92 at a cutoff of -1.275 or below, with a sensitivity of 92.8%, specificity of 62.5%, positive predictive value of 47.9%, and negative predictive value of 95.9%. The MBT had an AUROC of 0.91 at a cutoff of ≥0.42, with a sensitivity of 91.4%, specificity of 73.2%, positive predictive value of 52.0%, and negative predictive value of 96.4%.
Conclusions: Our results show that both Xpert-HR and the MBT are promising non-sputum-based point-of-care tests. The MBT met the World Health Organization target product profile for a triage test, which suggests it should be further developed.
Keywords: Biomarkers; diagnosis; point-of-care; triage; tuberculosis.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest . N. N. C., S. T. M., and G. W. hold patents for host blood protein signatures as triage tests for tuberculosis. All other authors report no potential conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . Global tuberculosis report 2024. Available at: https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tb-reports/globa.... Accessed 10 October 2024.
-
- Gupta-Wright A, Ha H, Abdulgadar S, et al. Evaluation of the Xpert MTB host response assay for the triage of patients with presumed pulmonary tuberculosis: a prospective diagnostic accuracy study in Viet Nam, India, the Philippines, Uganda, and South Africa. Lancet Glob Health 2024; 12:e226–e234. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

