Synthesis of AgInS2 quantum dots loaded with celastrol for induction of apoptosis and autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- PMID: 40238029
- PMCID: PMC12003245
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-02332-6
Synthesis of AgInS2 quantum dots loaded with celastrol for induction of apoptosis and autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Abstract
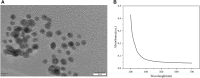
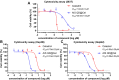
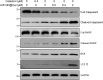
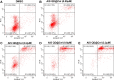
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a predominant form of liver cancer and one of the leading causes of cancer-related death globally. Therefore, there is an urgent need for innovative therapeutic strategies that target the molecular mechanisms underlying HCC progression and metastasis, aiming to improve treatment efficacy and patient survival. The natural product celastrol (Cel) has demonstrated inhibitory effects in various cancer cell lines. However, its clinical application has been hindered by high toxicity and a low safety threshold. Metal-free quantum dots (QDs), AgInS2 (AIS QDs) not only eliminate toxic risks associated with heavy metals but also exhibit high biocompatibility in the biomedical field. By developing AIS QD@Cel, an AIS QDs nano-delivery system for Cel, the cell selectivity and inhibitory effects of Cel on HCC were enhanced. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis revealed that AIS QDs can interact with Cel via amide bonds. The encapsulation rate of AIS QDs to Cel reached 27.5%. AIS QD@Cel eliminated toxicity on 293T and enhanced inhibition on HCC cells by over 10 times. Furthermore, the western blotting and flow cytometry experiments showed that AIS QD@Cel promoted apoptosis and autophagy signal pathway. Finally, transcriptome sequencing revealed that AIS QD@Cel effect on HCC by regulating gene expression involved in critical signaling pathways that are implicated in the progression of cancer. This strategy holds the potential to increase safety threshold and clinical applicability of Cel, offering significant clinical value for the treatment of HCC patients.
Keywords: AgInS2 quantum dots; Apoptosis; Autophagy; Celastrol; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Nanocarrier systems.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: The study is a commercial immortalised cell culture study and does not require ethics committee approval. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
