Low Th17 cells in patients with cystic fibrosis and allergic broncho-pulmonary aspergillosis
- PMID: 40238087
- PMCID: PMC12002360
- DOI: 10.1111/pai.70090
Low Th17 cells in patients with cystic fibrosis and allergic broncho-pulmonary aspergillosis
Abstract
Background: Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) is a hypersensitivity response to the allergens of Aspergillus fumigatus, which is the most frequently isolated fungus from the sputum of cystic fibrosis (CF) patients. Because a low number of Th17 lymphocytes is associated with the risk of fungal infections, we investigated inflammatory markers, Th17 cells, and T-cell polarization in CF patients with ABPA.
Methods: We analyzed the levels of inflammatory markers, blood counts, chemokines, cytokines, and T cell subsets in blood and sputum of CF subjects to elucidate the immunological factors associated with CF patients with Aspergillus fumigatus (AF) positive sputum (AFS+) or with ABPA.
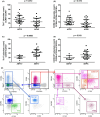
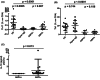
Results: We observed that AFS+ patients have higher sputum and blood IL-6 levels than AF-negative sputum (AFS-) patients. Analysis of blood memory T-helper subsets associated with Th1, Th2, and Th17 polarization among circulating CD45RA-/CD4+ memory T-cell subsets showed higher numbers of CCR4+/CCR6+/CXCR3- and CCR4+/CCR6+/CXCR3+ memory CD4 cells in AFS+ compared to AFS- subjects. Further analysis of Th17-related subsets and IL-17 secreting T cells in subjects with AFS+ showed that those with ABPA have statistically significantly lower levels of Th17 cells as compared to those without ABPA.
Conclusion: In CF, AF airway colonization is associated with increased blood counts of Th17-related subsets. However, CF patients with ABPA exhibit lower numbers of CCR4+/CCR6+/CXCR3+ memory CD4 cells and IL-17-secreting CD4 cells compared to control subjects and CF patients without AF sensitization.
Keywords: Th17 cells; allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis; cystic fibrosis; pediatrics.
© 2025 The Author(s). Pediatric Allergy and Immunology published by European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest related to the content of this manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IgE antibody to Aspergillus fumigatus recombinant allergens in cystic fibrosis patients with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis.Allergy. 2004 Feb;59(2):198-203. doi: 10.1046/j.1398-9995.2003.00310.x. Allergy. 2004. PMID: 14763934
-
The role of basophil activation test in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis and Aspergillus fumigatus sensitization in cystic fibrosis patients.J Cyst Fibros. 2016 Sep;15(5):587-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2016.02.004. Epub 2016 Feb 26. J Cyst Fibros. 2016. PMID: 26922860
-
The clinical presentations of pulmonary aspergillosis in children with cystic fibrosis - preliminary report.Dev Period Med. 2015 Jan-Mar;19(1):66-79. Dev Period Med. 2015. PMID: 26003072
-
Immunological mechanisms behind the cystic fibrosis-ABPA link.Med Mycol. 2009;47 Suppl 1:S183-91. doi: 10.1080/13693780802189938. Epub 2008 Jun 10. Med Mycol. 2009. PMID: 18651306 Review.
-
Allergic bronchopulmonary mycosis complicating cystic fibrosis.Semin Respir Infect. 1992 Sep;7(3):179-92. Semin Respir Infect. 1992. PMID: 1475542 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

