Perceived Health Impacts of Surface Mining: Local Perspectives from the Mining Communities in Libjo, Dinagat Islands, Philippines
- PMID: 40238380
- PMCID: PMC11942497
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph22030365
Perceived Health Impacts of Surface Mining: Local Perspectives from the Mining Communities in Libjo, Dinagat Islands, Philippines
Abstract
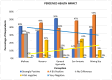
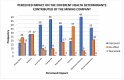
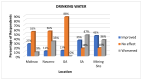
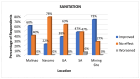
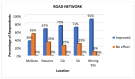
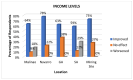
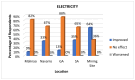
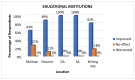
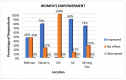
This study examines the perceived health impacts of a mining company on residents of Libjo, Dinagat Islands, Philippines, addressing a critical research gap in understanding the perceived health impacts of mining activities in underrepresented regions. The perceived health impacts of mining operations were examined using a qualitative research approach, employing semi-structured interviews. The interview instrument was developed to investigate how mining company activities impact key health determinants, such as water quality, sanitation, income, employment, infrastructure, education, and women's empowerment. The study was conducted across multiple sites at different distances from the mining area to further investigate the possible distance-based variations. The findings indicate that the mining company has positively impacted several areas, particularly income, employment, infrastructure, education, and women's empowerment. However, there were mixed perceptions regarding water quality and sanitation. The majority of respondents, particularly those who are near the mining sites, perceived a significant positive impact on health service delivery, attributing it to the company's support initiatives. Despite these positive impacts, the community expressed concerns about potential negative environmental consequences, such as air and water pollution, deforestation, land degradation, and noise pollution. This study reveals the complex relationship between mining operations and community health, emphasizing the importance of balancing economic benefits and environmental safety. The study further contributes to a deeper understanding of how mining operations affect the community's health and well-being and their potential distance-based variations.
Keywords: Libjo; health determinant; health impact; health service delivery; qualitative research; surface mining.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Deller S.C., Schreiber A. Mining and Community Economic Growth. Rev. Reg. Stud. 2012;42:121. doi: 10.52324/001c.8126. - DOI
-
- Mohsin M., Zhu Q., Naseem S., Sarfraz M., Ivascu L. Mining Industry Impact on Environmental Sustainability, Economic Growth, Social Interaction, and Public Health: An Application of Semi-Quantitative Mathematical Approach. Processes. 2021;9:972. doi: 10.3390/pr9060972. - DOI
-
- de Haes S., Lucas P. Environmental Impacts of Extraction and Processing of Raw Materials for the Energy Transition. [(accessed on 12 November 2024)]. Available online: http://www.yrdcpcn.org.cn/upload/2024/0821/a0e65c1a-97d9-40bc-80a5-f2f10....
-
- Moghimi Dehkordi M., Pournuroz Nodeh Z., Soleimani Dehkordi K., Salmanvandi H., Rasouli Khorjestan R., Ghaffarzadeh M. Soil, Air, and Water Pollution from Mining and Industrial Activities: Sources of Pollution, Environmental Impacts, and Prevention and Control Methods. Results Eng. 2024;23:102729. doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2024.102729. - DOI
-
- Petavratzi E., Kingman S., Lowndes I. Particulates from Mining Operations: A Review of Sources, Effects and Regulations. Miner. Eng. 2005;18:1183–1199. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2005.06.017. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

