Venetoclax-based regimens in octogenarian patients with CLL: efficacy, safety, and comparison to BTKi in a multicenter cohort
- PMID: 40239056
- PMCID: PMC12275189
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2025015818
Venetoclax-based regimens in octogenarian patients with CLL: efficacy, safety, and comparison to BTKi in a multicenter cohort
Abstract
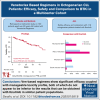
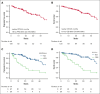
Octogenarians represent a significant fraction of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) but, despite the prevalence of the disease in this age group, limited data are available on the safety and efficacy of novel drugs in this subgroup. We conducted a multicenter retrospective study enrolling 120 octogenarian patients who received venetoclax (Ven) regimens in any line. Regarding efficacy, we found Ven to perform similarly to what is reported in younger patients with CLL, with an overall response rate of 91%, a complete response rate of 44%, and median progression-free survival of 44 months. Concerning safety, we report a toxicity profile that is consistent with previous reports, with most high-grade adverse events being of hematologic or infectious nature, given that 37% and 22% of patients experienced neutropenia or infections of grade 3 or higher. As part of our study, we compared the safety and efficacy data we collected with those obtained in a comparable Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi)-treated population. We found that these 2 treatments were comparable in terms of overall efficacy, barring a higher rate of complete responses with Ven; safety profiles were different among the 2 groups given that BTKi-treated patients had more cardiovascular toxicities (26% vs 4%) and Ven-treated subjects experienced more infectious events (82% vs 49%). Our data point out that Ven-based regimens are safe and effective in octogenarian patients with CLL despite their higher clinical complexity and comorbidity burden and should provide some basis for the design of prospective studies to further evaluate the optimal treatment regimen in this patient population.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: P.G. received honoraria from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Johnson & Johnson, Galapagos, Lilly/Loxo Oncology, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Roche; and research support from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Johnson & Johnson, and Lilly/Loxo Oncology. I.F. received research support from AbbVie, BeiGene, and Eli Lilly. M.V. received research support from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, and Johnson & Johnson. A. Sanna received research support from AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson. R. Marasca received research support from AbbVie, Johnson & Johnson, BeiGene, and AstraZeneca. A. Cuneo received research support from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Janssen, and Lilly. M. Marchetti received research support from Novartis, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Roche, Gilead, and GlaxoSmithKline. A.M.F. received research support from Janssen, BeiGene, AbbVie, and AstraZeneca. P.S. received research support from AbbVie, Johnson & Johnson, BeiGene, and AstraZeneca. C.V. received research support from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, and Janssen. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- National Cancer Institute Cancer Stat Facts: Leukemia — Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/clyl.html
-
- Cancer Research UK Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) incidence statistics. https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/s...
-
- Monnereau A, Troussard X, Belot A, et al. French Network of Cancer Registries (FRANCIM) Unbiased estimates of long-term net survival of hematological malignancy patients detailed by major subtypes in France. Int J Cancer. 2013;132(10):2378–2387. - PubMed
-
- Hallek M, Shanafelt TD, Eichhorst B. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. The Lancet. 2018;391(10129):1524–1537. - PubMed
-
- Hallek M, Cheson BD, Catovsky D, et al. iwCLL guidelines for diagnosis, indications for treatment, response assessment, and supportive management of CLL. Blood. 2018;131(25):2745–2760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials