Bismuth Meets Olefins: Ethylene Activation and Reversible Alkene Insertion into Bi─N Bonds
- PMID: 40239098
- PMCID: PMC12184319
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202505434
Bismuth Meets Olefins: Ethylene Activation and Reversible Alkene Insertion into Bi─N Bonds
Abstract
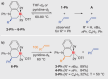
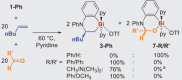
Owing to its fundamental properties as the parent olefin, its outstanding industrial relevance, and the challenges associated with its activation, ethylene remains a benchmark substrate, especially in main group chemistry. Here we report the unprecedented activation of ethylene and related simple α-olefins by well-defined cationic bismuth complexes. The polarization of a substrate by a softly Lewis-acidic central atom and a nucleophilic functional group positioned in a constrained geometry is for the first time exploited in the activation of ethylene and related olefins by compounds of a heavy p-block element. Mechanistic investigations point toward a coordination-insertion-reaction mechanism. The bonding properties of the cationic bismuth species facilitate unprecedented reversible reactivity patterns and unusual characteristics in chemoselectivity.
Keywords: Bismuth; Cationic species; Ethylene activation; Reversibility; Small molecule activation.
© 2025 The Author(s). Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Chum P. S., Swogger K. W., Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 797–819.
-
- Guo L., Liu W., Chen C., Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 2487–2494.
-
- Mol J., J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2004, 213, 39–45.
-
- Geilen F. M., Stochniol G., Peitz S., Schulte‐Koerne E., in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry (Eds: Bohnet M., Ullmann F.), Wiley‐VCH, Weinheim, 2003, pp. 1–13.
-
- Magano J., Dunetz J. R., Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2177–2250. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

