Leveraging Datathons to Teach AI in Undergraduate Medical Education: Case Study
- PMID: 40239213
- PMCID: PMC12017604
- DOI: 10.2196/63602
Leveraging Datathons to Teach AI in Undergraduate Medical Education: Case Study
Abstract
Background: As artificial intelligence and machine learning become increasingly influential in clinical practice, it is critical for future physicians to understand how such novel technologies will impact the delivery of patient care.
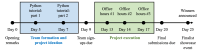
Objective: We describe 2 trainee-led, multi-institutional datathons as an effective means of teaching key data science and machine learning skills to medical trainees. We offer key insights on the practical implementation of such datathons and analyze experiences gained and lessons learned for future datathon initiatives.
Methods: We detail 2 recent datathons organized by MDplus, a national trainee-led nonprofit organization. To assess the efficacy of the datathon as an educational experience, an opt-in postdatathon survey was sent to all registered participants. Survey responses were deidentified and anonymized before downstream analysis to assess the quality of datathon experiences and areas for future work.
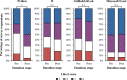
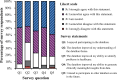
Results: Our digital datathons between 2023 and 2024 were attended by approximately 200 medical trainees across the United States. A diverse array of medical specialty interests was represented among participants, with 43% (21/49) of survey participants expressing an interest in internal medicine, 35% (17/49) in surgery, and 22% (11/49) in radiology. Participant skills in leveraging Python for analyzing medical datasets improved after the datathon, and survey respondents enjoyed participating in the datathon.
Conclusions: The datathon proved to be an effective and cost-effective means of providing medical trainees the opportunity to collaborate on data-driven projects in health care. Participants agreed that datathons improved their ability to generate clinically meaningful insights from data. Our results suggest that datathons can serve as valuable and effective educational experiences for medical trainees to become better skilled in leveraging data science and artificial intelligence for patient care.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; data science education; datathon; machine learning; undergraduate medical education.
© Michael Steven Yao, Lawrence Huang, Emily Leventhal, Clara Sun, Steve J Stephen, Lathan Liou. Originally published in JMIR Medical Education (https://mededu.jmir.org).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Pongdee T, Larson NB, Divekar R, Bielinski SJ, Liu H, Moon S. Automated identification of aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease using natural language processing and machine learning: algorithm development and evaluation study. JMIR AI. 2023 Jun 12;2:e44191. doi: 10.2196/44191. doi. Medline. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kendale S, Bishara A, Burns M, Solomon S, Corriere M, Mathis M. Machine learning for the prediction of procedural case durations developed using a large multicenter database: algorithm development and validation study. JMIR AI. 2023 Sep 8;2:e44909. doi: 10.2196/44909. doi. Medline. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

