Treatment of IL-18-binding protein biologics suppresses fibrotic progression in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis
- PMID: 40239621
- PMCID: PMC12047490
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102047
Treatment of IL-18-binding protein biologics suppresses fibrotic progression in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis
Abstract
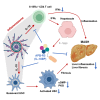
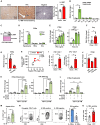
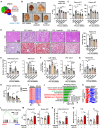
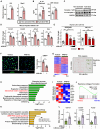
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) is a chronic liver disease characterized by inflammation and fibrosis, with enhanced interleukin-18 (IL-18) signaling. IL-18-binding protein (IL-18BP) neutralizes IL-18, but its therapeutic potential in MASH is unclear. We find elevated IL-18BP and IL-18 levels in patients with MASH and mice, with free IL-18 correlating with disease severity. IL-18 stimulates interferon-gamma (IFNγ) production in CD4 T cells, increasing hepatic IL-18BP. IL-18BP-deficient mice show worsened liver inflammation and fibrosis. We develop a human IL-18BP biologics (APB-R3) and inject it to mice to evaluate its pharmacologic efficacy. APB-R3 significantly improves MASH in reducing fibrosis and inflammation and inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation via the cGMP pathway. This study proposes that abrogation of IL-18 signaling by boosting IL-18BP can strongly inhibit the development of MASH-induced fibrosis, and our engineered IL-18BP biologics can become a promising therapeutic candidate for curing MASH.
Keywords: APB-R3; IFNγ; IL-18BP; MASH; fibrosis; hepatic stellate cell.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests At the time of submission, J.P., S.C., J.H., S.-M.K., and S.-H.C. were employees of AprilBio Co., Ltd (Chuncheon, South Korea).
Figures




References
-
- Singh S., Allen A.M., Wang Z., Prokop L.J., Murad M.H., Loomba R. Fibrosis progression in nonalcoholic fatty liver vs nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of paired-biopsy studies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015;13:643–e40. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2014.04.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Inzaugarat M.E., Johnson C.D., Holtmann T.M., McGeough M.D., Trautwein C., Papouchado B.G., Schwabe R., Hoffman H.M., Wree A., Feldstein A.E. NLR Family Pyrin Domain-Containing 3 Inflammasome Activation in Hepatic Stellate Cells Induces Liver Fibrosis in Mice. Hepatology. 2019;69:845–859. doi: 10.1002/hep.30252. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

